Amino acid neurotransmitter
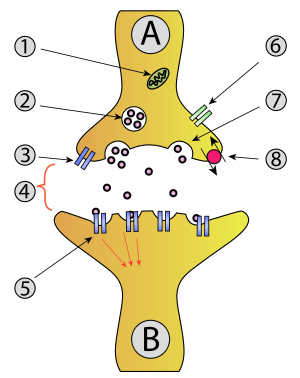 | Activity at an axon terminal: Neuron A is transmitting a signal at the axon terminal to neuron B (receiving). Features: 1. Mitochondrion. 2. synaptic vesicle with neurotransmitters. 3. Autoreceptor. 4. Synapse with neurotransmitter released (serotonin). 5. Postsynaptic receptors activated by neurotransmitter (induction of a postsynaptic potential). 6. Calcium channel. 7. Exocytosis of a vesicle. 8. Recaptured neurotransmitter. |
An amino acid neurotransmitter is an amino acid which is able to transmit a nerve message across a synapse. Neurotransmitters (chemicals) are packaged into vesicles that cluster beneath the axon terminal membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse in a process called endocytosis.[1]
Amino acid neurotransmitter release (exocytosis) is dependent upon calcium Ca2+ and is a presynaptic response. There are inhibitory amino acids (IAA) or excitatory amino acids (EAA). Some EAA are L-Glutamate, L-Aspartate, L-Cysteine, and L-Homocysteine.[2] These neurotransmitter systems will activate post-synaptic cells.[3] Some IAA include GABA, Glycine, β-Alanine, and Taurine.[2] The IAA depress the activity of post-synaptic cells.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Axon Terminal : on Medical Dictionary Online". Archived from the original on 14 January 2009. Retrieved 2008-12-25.
- 1 2 Foye, William O.; Lemke, Thomas L. (2007). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. David A. Williams. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 446. ISBN 978-0-7817-6879-5.
- 1 2 D'haenen, Hugo; den Boer, Johan A. (2002). Biological Psychiatry (digitised online by Google books). Paul Willner. John Wiley and Sons. p. 415. ISBN 978-0-471-49198-9. Retrieved 2008-12-26.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/23/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.