V1500 Cygni
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 21h 11m 36.6s |
| Declination | +48° 09′ 02.1″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 1.7Max. 18Min. |
| Characteristics | |
| Astrometry | |
| Distance | 6,360 ly |
| Other designations | |
V1500 Cygni or Nova Cygni 1975 was a bright nova occurring in 1975 in the constellation Cygnus. It had the second highest intrinsic brightness of any nova of the 20th century, exceeded only by CP Puppis in 1942.[1]
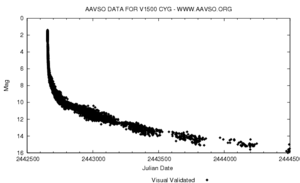
V1500 Cygni was discovered on August 29 and reached magnitude 1.7 on the next day. It remained visible to the naked eye for about a week, and 680 days after maximum the star had dimmed by 12.5 magnitudes.
It is an AM Herculis type star, consisting of a red dwarf secondary depositing a stream of material onto a highly magnetized white dwarf primary. The distance of the V1500 Cygni was calculated in 1977 by the McDonald Observatory at 1.95 kiloparsecs (6,360 light years).[2] Additionally, V1500 Cyg was the first asynchronous polar to be discovered. This distinction refers to the fact that the white dwarf's spin period is slightly different than the binary orbital period.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "V1500 Cyg (Nova Cygni 1975)", American Association of Variable Star Observers
- ↑ Ferland, G. J. (1977). "The interstellar reddening and distance of Nova Cygni 1975 /V1500 Cygni/". Astrophysical Journal. 215: 873. Bibcode:1977ApJ...215..873F. doi:10.1086/155424.
- ↑ Stockman, H. S.; Schmidt, Gary D.; Lamb, D. Q. (1988). "V1500 Cygni - Discovery of a magnetic nova". The Astrophysical Journal. 332: 282. Bibcode:1988ApJ...332..282S. doi:10.1086/166652.
Further reading
- Ferland GJ; Tomkin J; Woodman J (1976). "Continuum variability in Nova Cygni 1975". Nature. 264 (5587): 627–9. Bibcode:1976Natur.264..627F. doi:10.1038/264627a0.
External links
- "Detail for V1500 Cygni". The International Variable Star Index. Retrieved 2008-09-09.
- "Nova Cygni 1975 (V1500 Cygni)". The Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy and Spaceflight. Retrieved 2005-08-12.
- "V1500 Cyg (Nova Cygni 1975)". American Association of Variable Star Observers. Retrieved 2010-08-29.