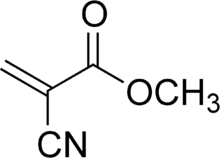
Methyl cyanoacrylate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl 2-cyanoprop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
Methyl 2-cyanopropenoate Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate 2-Cyano-2-propenoic acid methyl ester MCA Methyl alpha-cyanoacrylate Mecrylate Ad/here Adhere CA 7 Cemedine 3000 Coapt Cyanobond 5000 Eastman 910 Fimofix P 1048 Mecrilat Mecrilate Sicomet 7000 Three Bond 1701[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 137-05-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 8387 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.796 |
| PubChem | 8711 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H5NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 111.1 g/mol |
| Density | 1.1 |
| Melting point | −40 °C (−40 °F; 233 K) |
| Boiling point | 48 to 49 °C (118 to 120 °F; 321 to 322 K) (2.5-2.7 mm Hg) |
| 30% (20°C)[2] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.2 mmHg (25°C)[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 79 °C; 174 °F; 352 K [2] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[2] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 2 ppm (8 mg/m3) ST 4 ppm (16 mg/m3)[2] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[2] |
| Related compounds | |
| Related Cyanoacrylates |
Ethyl cyanoacrylate Butyl cyanoacrylate Octyl cyanoacrylate |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Methyl cyanoacrylate (MCA) is an organic compound that contains several functional groups, a methyl ester, a nitrile, and an alkene. It is a colorless liquid with low viscosity. Its chief use is as the main component of cyanoacrylate glues.[3] It can be encountered under many trade names. Methyl cyanoacrylate is less commonly encountered than ethyl cyanoacrylate.
It is soluble in acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, nitromethane, and dichloromethane.[4] MCA polymerizes rapidly in presence of moisture.
Safety
Heating the polymer causes depolymerization of the cured MCA, producing gaseous products strongly irritant to lungs and eyes. In regards to occupational exposure to MCA, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health recommends workers do not exceed exposures over 2 ppm (8 mg/m3) over an eight-hour workshift, or over 4ppm (16 mg/m3) over a short-term exposure.[5]
References
- ↑ Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate at Cameo Chemicals
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0405". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate at Inchem.org
- ↑ Palm Labs Adhesives
- ↑ CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards