Workington railway station
| Workington | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | |
| Place | Workington |
| Local authority | Allerdale |
| Coordinates | 54°38′42″N 3°33′29″W / 54.645°N 3.558°WCoordinates: 54°38′42″N 3°33′29″W / 54.645°N 3.558°W |
| Grid reference | NX995288 |
| Operations | |
| Station code | WKG |
| Managed by | Northern |
| Number of platforms | 2 |
| DfT category | E |
|
Live arrivals/departures, station information and onward connections from National Rail Enquiries | |
| Annual rail passenger usage* | |
| 2010/11 |
|
| 2011/12 |
|
| 2012/13 |
|
| 2013/14 |
|
| 2014/15 |
|
| National Rail – UK railway stations | |
| * Annual estimated passenger usage based on sales of tickets in stated financial year(s) which end or originate at Workington from Office of Rail and Road statistics. Methodology may vary year on year. | |
|
| |
Railway stations in Workington | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Workington railway station serves the town of Workington in Cumbria, England. The railway station is a stop on the scenic Cumbrian Coast Line 33 miles (53 km) south west of Carlisle. Some through trains to the Furness Line and from Sunderland stop here. It is operated by Northern who provide all passenger train services.
History and data
History

The first Workington station on the Cumbrian Coast Line was built in the area known as Priestgate Marsh for the Whitehaven Junction Railway. Although the WJR was opened from Maryport to Workington in 1845[1] the WJR was advertising for tenders for building the station at Workington in October 1846.[2] The WJR station had a single arrival and departure platform (the line was single until 1860) and no platform canopy "the platform is open to the prevailing winds, and " (we) " believe Workington is the only first-class station in Great Britain so unprovided with shelter" complained the Workington town trustees in 1858.[3] In 1854 misset points led to a Maryport-Whitehaven goods train being routed into the end bay used by the Workington - Cockermouth trains: the goods train demolished the buffers and "dashed through" the booking office, the porter's office, and the gentleman's waiting room, carrying away the street wall of the station building, and finally coming to rest at the far wall of the ladies' waiting room. The booking office clerk having seen the train approaching, no lives were lost but "the station" reported the Cumberland Pacquet "is of course a perfect wreck" [4] and had to be re-built. (Immediately after the accident, the gas supply to the station was turned off at the meter, but it was noted that three gas lights continued to burn - the town trustees (who owned the town gasworks) declined to restore the supply until the WJR gave a satisfactory explanation or adequate compensation.)[5]
The London & North Western Railway took over the Whitehaven Junction and Workington & Cockermouth lines in 1866, and replaced the WJR station. The LNWR station was extended further north than the WJR one, with its principal entrance now facing Station Road; a footpath through the goods yard was suppressed, and South Quay (linking the harbour with the town) was carried over the railway on a bridge, replacing a dangerous level crossing.
At the height of railway development, two other stations served Workington: Workington Bridge on the Cockermouth and Workington Railway, and Workington Central on the Cleator and Workington Junction Railway. - both are now closed. The station on the coast line retained first claim on Workington, but after the opening of Workington Central could be distinguished from it by local papers as 'the Workington low railway station':[6] it could be formally known as Workington LNWR (to distinguish it from Workington Central, Workington Bridge was also an LNWR station) or (post-grouping, when all three stations were LMS) as Workington Main; with the closure of the other stations it has reverted (both formally and informally) to being simply 'Workington' railway station. Trains from the Cockermouth and Keswick direction ended with the closure of that branch to all traffic in April 1966, the line having fallen victim to the Beeching Axe.
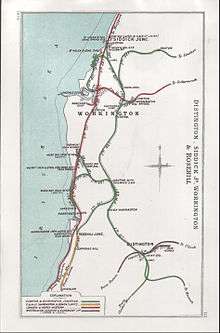
Layout
The station was built with yellow Crewe bricks and had four tracks running though the station. Two of the tracks which are not served by platforms were once used to stable Travelling Post Office carriages. There was also a twelve road engine shed, wagon repair shops, a coaling stage, a goods shed and a stable block, all built with local sandstone. In LMS days, a new turntable was installed behind the engine shed. In British Railways days the engine shed was rebuilt with a new roof and ferro-concrete coaling stage and an ash disposal plant was built near to the new turntable. The road approach to the station entrance was remodelled in BR days when the highways near to the station were upgraded. Immediately adjacent to the southbound platform are two carriage sidings, used for stabling & servicing empty DMU sets overnight and at weekends. There is also a train crew depot here.
Facilities
The station is staffed throughout the week (closed in the evenings). There are waiting rooms and covered waiting areas on each platform, which are linked via footbridge. Step-free access is available to both platforms via ramps and a foot level crossing, though this is only open when station staff are present.[7] Outside these times, the only available access routes have steps. A P.A system and digital information screens provide train running information.
Temporary Workington North station
As a consequence of the November 2009 Great Britain and Ireland floods, Network Rail built a temporary additional station 1 mile (1.6 km) from the existing station on waste ground off the A596 adjacent to a business park.[8] An additional hourly shuttle train (composed of a locomotive and at least three former inter-city mainline coaches) operated by Cumbrian-based Direct Rail Services on behalf of Northern Rail, running from Workington northbound to Maryport was created in the aftermath of the floods.[9][10][11] This service started on 30 November 2009 and ran until 28 May 2010.[12] It was initially funded by the Department for Transport at a cost of £216,000. All services between Workington and Maryport were free of charge for this period.[13]
Services
There is generally an hourly service northbound to Carlisle and southbound to Whitehaven with most daytime trains going onwards to Barrow-in-Furness.[14] On Sundays, there are four trains each way between Carlisle and Whitehaven only - a modest improvement on the three departures each way that ran prior to the December 2013 timetable change.
| Preceding station | Following station | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Cumbrian Coast Line | ||||
| Historical railways | ||||
Line open, station closed | Northern Workington North railway station 2009-10 Temporary Service | Line and station open |
||
| Disused railways | ||||
| Workington Bridge Line and station closed |
London and North Western Railway Cockermouth & Workington Railway |
Terminus | ||
References
- ↑ "Railway Intelligence - Local - Partial Opening of the Whitehaven Junction Railway". Carlisle Patriot. 14 November 1845. p. 3.
- ↑ (advertisement): "Whitehaven Junction Railway - Tenders for Building the Station at Workington". Cumberland Pacquet, and Ware's Whitehaven Advertiser. 20 October 1846. p. 1.
- ↑ "Workington Town Trustees". Whitehaven News. 25 March 1858. p. 2.
- ↑ "Serious Accident on the Whitehaven Junction Railway". Cumberland Pacquet, and Ware's Whitehaven Advertiser. 13 December 1853. p. 3.
- ↑ "A Railway Station in Darkness". Carlisle Patriot. 21 January 1854. p. 5.
- ↑ e.g. "Assaulting a Railway Official". Cumberland Pacquet, and Ware's Whitehaven Advertiser. 14 November 1889. p. 5.
- ↑ Workington station facilities National Rail Enquiries; Retrieved 2 December 2016
- ↑ "Station hope for town cut in two". BBC News. 24 November 2009.
- ↑ Hume, Colette (30 November 2009). "Workington gets new rail station after Cumbria flood". BBC News Online. Retrieved 30 November 2009.
- ↑ "Free shuttle train between Workington and Maryport". Times & Star. Retrieved 29 November 2009.
- ↑ "New shuttle service on Cumbrian coast from Monday 30 November". Northern Rail. Archived from the original on 29 November 2009.
- ↑ "FFREE CUMBRIA FLOODS TRAIN SERVICE TO FINISH NEXT WEEK". Carlisle Times and Star. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- ↑ "New hourly train to help reunite Cumbrian community". Department for Transport. 30 November 2009.
- ↑ Table 100 National Rail timetable, December 2016
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Workington railway station. |
- Train times and station information for Workington railway station from National Rail