Thyroarytenoid muscle
| Thyroarytenoid muscle | |
|---|---|
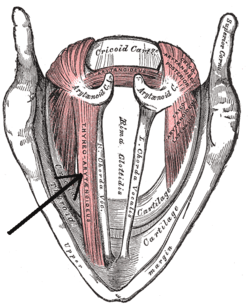 Muscles of the larynx, seen from above. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Inner surface of the thyroid cartilage (anterior aspect) |
| Insertion | Anterior surface of arytenoid cartilage |
| Nerve | Recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus |
| Actions | Helps to reduce tension on the vocal folds during speech to decrease pitch |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus thyroarytenoideus |
| TA | A06.2.08.008 |
| FMA | 46588 |
The thyroarytenoid muscle is a broad, thin muscle that forms the body of the vocal fold and that supports the wall of the ventricle and its appendix. It functions to relax the vocal folds.
Structure
It arises in front from the lower half of the angle of the thyroid cartilage, and from the middle cricothyroid ligament.
Its fibers pass backward and laterally, to be inserted into the base and anterior surface of the arytenoid cartilage.
Parts
The lower and deeper fibers of the muscle can be differentiated as a triangular band which is inserted into the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage, and into the adjacent portion of its anterior surface; it is termed the Vocalis, and lies parallel with the vocal ligament, to which it is adherent.
The vocal muscle is the upper portion of the thyroarytenoid muscle which is primarily involved in producing speech.
A considerable number of the fibers of the thyroarytenoid muscle are prolonged into the aryepiglottic fold, where some of them become lost, while others are continued to the margin of the epiglottis. They have received a distinctive name, thyroepiglottic muscle, thyreoepiglotticus or thyroepiglottic, and are sometimes described as a separate muscle.
A few fibers extend along the wall of the ventricle from the lateral wall of the arytenoid cartilage to the side of the epiglottis and constitute the ventricularis muscle.
Function
The thyroarytenoid muscle, consisting of two parts having different attachments and different directions, are rather complicated as regards their action.
Their main use is to draw the arytenoid cartilages forward toward the thyroid, and thus relax and shorten the vocal folds.
But, owing to the connection of the deeper portion with the vocal fold, this part, if acting separately, is supposed to modify its elasticity and tension, while the lateral portion rotates the arytenoid cartilage inward, and thus narrows the rima glottidis by bringing the two vocal folds together.
Additional images
 Muscles of larynx. Side view. Right lamina of thyroid cartilage removed.
Muscles of larynx. Side view. Right lamina of thyroid cartilage removed.- Cross sectional cut of vocalis muscle
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:32:st-0605 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Atlas image: rsa4p5 at the University of Michigan Health System