Tropical Storm Higos (2008)
| Tropical storm (JMA scale) | |
|---|---|
| Tropical storm (Saffir–Simpson scale) | |
 Tropical Storm Higos near peak intensity | |
| Formed | September 29, 2008 |
| Dissipated | October 6, 2008 |
| Highest winds |
10-minute sustained: 65 km/h (40 mph) 1-minute sustained: 75 km/h (45 mph) |
| Lowest pressure | 998 hPa (mbar); 29.47 inHg |
| Fatalities | Unknown |
| Damage | $6.5 million (2008 USD) |
| Areas affected | Philippines, China |
| Part of the 2008 Pacific typhoon season | |
Tropical Storm Higos, known in the Philippines as Tropical Storm Pablo, was a tropical storm during the 2008 Pacific typhoon season. The name "Higos" is the Chamorro word for fig.[1]
Meteorological history

On September 27 a tropical disturbance formed in the Philippine Sea to the east of Mindanao, in the Philippines. During the next day the JTWC issued a TCFA on the tropical disturbance. Early on September 29 the JMA designated the disturbance as a tropical depression. Later that day, both PAGASA and the JTWC designated the disturbance as a tropical depression, with PAGASA naming the depression as Pablo whilst the JTWC designated it as Tropical Depression 21W. The JTWC upgraded the depression to a tropical storm early in the afternoon. The JMA followed shortly after and upgraded the system to Tropical Storm Higos early on September 30. Higos tracked towards the northwest and made landfall in the eastern Philippines (on Samar island) on October 1. Higos tracked over the Philippines as a tropical storm (but PAGASA downgraded it as a tropical depression) for most of the day before moving out over open waters. Once out over water, the JTWC downgraded Higos to a tropical depression, however, the JMA kept it as a tropical storm. As Higos neared landfall, it suddenly relocated, paralleling the northeastern coast of Hainan, China. The storm later made landfall on October 4 around 2 a.m. (CST) on the northern coastline of the island. JMA then issued its final advisory as Higos weakened to a tropical depression. The JTWC followed 12 hours later.
Preparations, Warnings and Impact
Preparations
Ferry services on Qiongzhou Strait in south China were suspended and authorities in two airports in Hainan Province: Meilan International Airport in Haikou, the provincial capital, and Fenghuang (Phoenix) International Airport in Sanya, a seaside resort on the southern tip of the island, managed to keep arrivals and departures at their respective airports going.
Highest Public Storm Warning Signal
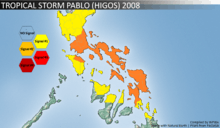
| PSWS# | LUZON | VISAYAS | MINDANAO |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSWS #2 | Metro Manila, Rizal, Batangas, Cavite, Laguna, Quezon, Polilio Is., Marinduque, Northern Mindoro Oriental, Masbate, Camarines Provinces, Albay, Sorsogon, Catanduanes | Biliran, Samar Provinces, Leyte | None |
| PSWS #1 | Pangasinan, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Quirino, Aurora, Bulacan, Bataan, Zambales, Pampanga, Tarlac, Lubang Is. Rest of Mindoro Oriental, Mindoro Occidental, Romblon | Aklan, Capiz, Northern Iloilo, Northern Negros Occidental, Northern Cebu. Southern Leyte | Dinagat Island, Surigao del Norte, Siargao Is. |
Warnings
China issued an orange alert on for Higos and the State Flood Control and Drought Relief Headquarters activated a third degree emergency response on Friday to prevent flooding,[2] while in Hong Kong, the Standby Signal No. 1 was issued at 7.30 p.m. on October 2 when Higos was about 700 km south of Hong Kong. All tropical cyclone warning signals were cancelled at 10.30 p.m. on October 4 as Higos made landfall over western Guangdong and weakened.[3]
Impact
In Hong Kong, a sheet of glass fell off from a shopping centre in Tsim Sha Tsui when the Strong Monsoon Signal was in force. Two vehicles were damaged and a person was slightly injured during the incident. In addition, a scaffolding was reported loose in Kowloon Bay.[4] Higos caused $6.5 million in damage to the province of Xinhua, however its heavy rainfall may have stopped a potential drought from starting.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.jma.go.jp/jma/jma-eng/jma-center/rsmc-hp-pub-eg/tyname.html#Column%20III
- ↑ http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2008-10/03/content_7075779.htm
- ↑ http://www.hko.gov.hk/informtc/higos/report.htm
- ↑ http://www.hko.gov.hk/informtc/higos/report.htm
- ↑ http://www.uclick.com/widgets/ew/081010/ew081010e.html
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tropical Storm Higos (2008). |
- JMA General Information of Tropical Storm Higos (0817) from Digital Typhoon
- JMA Best Track Data of Tropical Storm Higos (0817) (Japanese)
- JTWC Best Track Data of Tropical Storm 21W (Higos)
- 21W.HIGOS from the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory
