Trang Province
| Trang ตรัง | ||
|---|---|---|
| Province | ||
|
Ko Lao Liang Phi in Mu Ko Phetra National Park | ||
| ||
 Map of Thailand highlighting Trang Province | ||
| Country |
| |
| Capital | Trang | |
| Government | ||
| • Governor | Siriphat Phatthakun (since October 2016) | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 4,917.5 km2 (1,898.7 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | Ranked 44th | |
| Population (2014) | ||
| • Total | 638,746 | |
| • Rank | Ranked 40th | |
| • Density | 130/km2 (340/sq mi) | |
| • Density rank | Ranked 36th | |
| Time zone | ICT (UTC+7) | |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-92 | |
Trang (Thai: ตรัง, pronounced [trāŋ]), also called Mueang Thap Thiang, is one of the southern provinces (changwat) of Thailand, on the west side of the Malay Peninsula facing the Strait of Malacca. Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Krabi, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Phatthalung, and Satun.
Trang was formerly a port involved in foreign trade. It was the first place where rubber was planted in Thailand. Phraya Ratsadanupradit Mahison Phakdi brought rubber saplings from Malaya and planted them here in 1899, and rubber is now an important export of the country. The Trang River flows through the province from its origin in the Khao Luang mountain range, and the Palian River flows from the Banthat mountains. The province of Trang has an area of approximately 5,000 square km and 199 km of Strait of Malacca shoreline.[1]
Geography
The province is on the coast of the Strait of Malacca, and contains 46 islands together with the mainland area. There are only few plains, and most of the area is hills. The Khao Luang and the Banthat mountain range are the sources of the two main rivers of the province, the Trang River and the Palian River.
The southern coast of the province is protected in the Mu Ko Phetra National Park. The estuary of the Trang River together with the Hat Chao Mai Marine National Park[2] and Ko Libong Non-hunting Area are also registered Ramsar wetlands.
History
Trang was an important seaport in southern Thailand. Legend says that ships always arrived in the morning, which led to the town's name. "Trang" derives from the Malay word for 'light' (terang). The province was once a part of the ancient Kedah Tua Kingdom, a Kedahan Malay kingdom.
According to cultural records Trang was one of 12 satellite towns that existed about 900 years ago, but it was during the reign of King Rama II that the province got its first governor. The first Westerner to arrive in Trang was Captain James Low, who came in 1838 to negotiate commercial benefits.
The original town was in Khuanthani (now a tambon in district Kantang). In 1893, the governor, Phraya Ratsadanupradit Mahison Phakdi, also known as Khaw Sim Bee na Ranong, decided to make Trang an important seaport and relocated the town to Kantang District on the Trang River delta. It was moved again to its present location 26 km inland in 1916 by King Rama VI because of repeated flooding.
Trang was the first area of Thailand where rubber trees were planted, brought there by governor Phraya Ratsadanupradit Mahison Phakdi from British Malaya in 1899.
Symbols
The seal of the province shows a lighthouse bridge above a sea of waves. The lighthouse bridge refers to Trang as a seaport trading with foreign countries.[3]
The provincial symbolic flower and tree is the green ebony (Jacaranda filicifolia). The plant was imported from Australia by the same governor who imported the rubber tree, and it quickly got the name "si trang" by the citizens.
The provincial slogan เมืองพระยารัษฏา ชาวประชาใจกว้าง ถิ่นกำเนิดยางพารา เด่นสง่าดอกศรีตรัง ปะการังใต้ทะเล เสน่ห์หาดทรายงาม น้ำตกสวยตระการตา translates as "Phraya Rasda's town, generous people, delicious roast pork, the first city where para rubber was planted, the Si Trang provincial flower, underwater coral reefs, scenic beaches and waterfalls."[3]
Administrative divisions
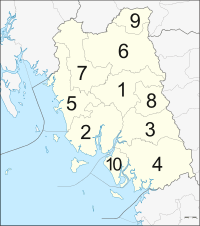
Trang is divided into 10 districts (amphoe). These are further subdivided into 87 sub-districts (tambon) and 697 villages (muban).
|
 |
Transportation
Air: Trang Airport is 7 km from Trang town centre.[4] It is served by Thailand AirAsia and Nok Air, with flights to Bangkok.
Rail: Trang is one of the southern destinations offering trains to Bangkok's Hualamphong Station. Starting from Thung Song Station in Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, this southwestern route passes Huay Yod station to Muang Station and ends at Kan Tang terminal in Trang.
Road: Major roads to and from Trang are:
- Highway 4 (Bangkok—Chumphon) to Highway 41 (Surat Thani—Thung Song—Huai Yot—Trang), a distance of 828 kilometres.
- Highway 4 (Bangkok—Chumphon) to Ranong—Phang Nga—Krabi—Trang, a distance of 1,020 kilometres.
- Highway 404-416 (Satun—Palian—Trang), a distance of 140 kilometres.
- Highway 4-407 (Hat Yai—Phatthalung—Trang), a distance of 148 kilometres.
- Highway 4-402 (Phuket—Phang Nga—Krabi—Trang), a distance of 312 kilometres.
Bus:There are buses to and from Trang to Bangkok and main provinces (Phuket, Hat Yai, Krabi, Nakhon Si Thammarat, and Satun).
Boats to islands: Trang has four piers for boats to the islands: Pak Meng Pier, Ban Chao Mai Pier, Klong Son Pier, and Kuan Thung Kuu Pier.
Education
Secondary schools:
- Wichienmatu School วิเชียรมาตุ
- Wichienmatu 2 School วิเชียรมาตุ 2
- Wichienmatu 3 School วิเชียรมาตุ 3
- Saparachinee School สภาราชินี
- Saparachinee 2 School สภาราชินี 2
- Princess Chulabhorn's College, Trang จุฬาภรณ์ราชวิทยาลัย
- Sport School, Trang โรงเรียนกีฬาตรัง
- Buranarumluk School บูรณะรำลึก
- Darunothai School ดรุโณทัย
- Trang vittaya School ตรังวิทยา
- Trangchristiensuksa ตรังคริสเตียนศึกษา
- Matayomsuksa Watkuanwisetmulaniti School มัธยมศึกษาวัดควนวิเศษ มูลนิธิ
- Kantangpittayakorn School กันตังพิทยากร
- Kantangratsadasuksa School กันตังรัษฎาศึกษา
- Yantakhao Ratchanupatham School ย่านตาขาวรัฐชนูปถัมภ์
- Palean padungsit School ปะเหลียนผดุงศิษย์
- Kantapittayakarn School คันธพิทยาคาร
- Sikao prachapadungvit School สิเกาประชาผดุงวิทย์
- Wangviset School วังวิเศษ
- Huayyot School ห้วยยอด
- Lampurareungvit School ลำภูราเรืองวิทย์
- Nampud School น้ำผุด
- Ratsada School รัษฎา
- Huaynang ratsadornbamrung School ห้วยนางราษฎรบำรุง
- Ratsadanupradit anusorn School รัษฎานุประดิษย์อนุสรณ์
- Nayong vittayakom School นาโยงวิทยาคม
- Sawatratanapimuk School สวัสดิ์รัตนาภิมุข
- Thungnonghang prachason School ทุ่งหนองแห้งประชาสรรค์
- Hatsumran vittayakom School หาดสำราญวิทยาคม
- Trang polytechnic School ตรังโปลีเทคนิค
Higher education:
- Rajamangala University of Technology Srivijaya (Trang campus) bachelor's degrees in fisheries, marine science, aquaculture, environmental science, and tourism
- Prince of Songkla University (Trang campus) bachelor's degree in accounting administration, IT, MBA
- Ramkhamhaeng University (Trang campus) bachelor's and master's degrees
- Suan Dusit Rajabhat University (Trang center) bachelor's degree
- Boromrajonane College of Nursing, bachelor's degree and diploma
- Sirindhorn College of Public Health, bachelor's degree and diploma
- Trang Technical College, diploma
- Trang College of Agricultural and Technology, diploma
- Trang Polytechnic College, diploma
- Siam Commercial College, diploma
Healthcare
- Trang Hospital (government)
- Watanapat Hospital (private)
- Trang Ruampat Hospital (private)
References
- ↑ "Trang". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ↑ "Hat Chao Mai National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- 1 2 "Symbol of Trang". OSM Andamnan: The Office of Strategy Management for Southern Province Cluster. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ↑ "Trang Airport". Department of Civil Aviation (DCA): Trang. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
External links
 Trang travel guide from Wikivoyage
Trang travel guide from Wikivoyage- Provincial website
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to [[commons:Category:Trang|]]. |
 |
Krabi Province | Nakhon Si Thammarat Province |  | |
| |
Phattalung Province | |||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Strait of Malacca | Satun Province |
Coordinates: 7°33′29″N 99°36′42″E / 7.55806°N 99.61167°E

