Thiocarboxylic acid


Thiocarboxylic acids are organosulfur compounds related to carboxylic acids by replacement of one of the oxygen atoms with a sulfur atom. Two tautomers, RC(S)OH and RC(O)SH, are possible.[1] They are called "carbothioic O-acid" and "carbothioic S-acid" respectively; of these carbothioic S-acid tautomer is far more common.
In the laboratory the most common thiocarboxylic acid is thioacetic acid. A naturally occurring thiocarboxylic acid is 2,6-pyridinedicarbothioic acid, a siderophore.
Thiocarboxylic acids are typically prepared by salt metathesis from the acid chloride, as in the following conversion of benzoyl chloride to thiobenzoic acid using potassium hydrosulfide according to the following idealized equation:[2]
- C6H5C(O)Cl + KSH → C6H5C(O)SH + KCl
Reactions
Thiocarboxylic acids are more acidic than the analogous carboxylic acids. Thus at neutral pH, the acids are fully ionized. Salts of their conjugate bases, e.g. potassium thioacetate, serve as reagents for installing thiol groups via the displacement of alkyl halides to give the thioester, which in turn are susceptible to hydrolysis.
Thiocarboxylic acids react with various nitrogen functional groups, such as organic azide, nitro, and isocyanate compounds, to give amides under mild conditions.[3][4] This method avoids needing a highly nucleophilic aniline or other amine to initiate an amide-forming acyl substitution, but requires synthesis and handling of the unstable thiocarboxylic acid.[4] Unlike the Schmidt reaction or other nucleophilic-attack pathways, the reaction with an aryl or alkyl azide begins with a [3+2] cycloaddition; the resulting heterocycle expels N2 and the sulfur atom to give the monosubstituted amide.[3]
Dithiocarboxylic acids
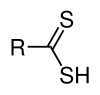
Dithiocarboxylic acids, with the formula RCS2H, are less common than the monothio derivatives. Such compounds are commonly prepared by the reaction of carbon disulfide with a Grignard reagent:[5]
- RMgX + CS2 → RCS2MgX
- RCS2MgX + HCl → RCS2H + MgXCl
This reaction is comparable to the formation of carboxylic acids using a Grignard and carbon dioxide.
See also
References
- ↑ Cremlyn, R.J. (1996). An introduction to organosulfur chemistry. Chichester: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-95512-4.
- ↑ Noble, Jr., Paul; Tarbell, D. S. (1963). "Thiobenzoic Acid". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 4, p. 924
- 1 2 "21.1.2.6.1: Variation 1: From thiocarboxylic acids". Science of Synthesis: Houben–Weyl Methods of Molecular Transformations. Vol. 21: Three Carbon-Heteroatom Bonds: Amides and Derivatives; Peptides; Lactams. Georg Thieme Verlag. 2005. pp. 52–54. ISBN 9783131719515.
- 1 2 Xie, Sheng; Zhang, Yang; Ramström, Olof; Yan, Mingdi (2016). "Base-catalyzed synthesis of aryl amides from aryl azides and aldehydes". Chem. Sci. 7: 713–718. doi:10.1039/C5SC03510D.
- ↑ Ramadas, S. R.; Srinivasan, P. S.; Ramachandran, J.; Sastry, V. V. S. K. (1983). "Methods of Synthesis of Dithiocarboxylic Acids and Esters". Synthesis. 1983 (08): 605–622. doi:10.1055/s-1983-30446.