Streptomyces isolates
Streptomyces isolates have yielded the majority of human, animal, and agricultural antibiotics, as well as a number of fundamental chemotherapy medicines. Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus of actinobacteria, producing chemotherapy, antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic drugs, and immunosuppressants.[1] Streptomyces isolates are typically initiated with the aerial hyphal formation from the mycelium.
Anticancer medicines
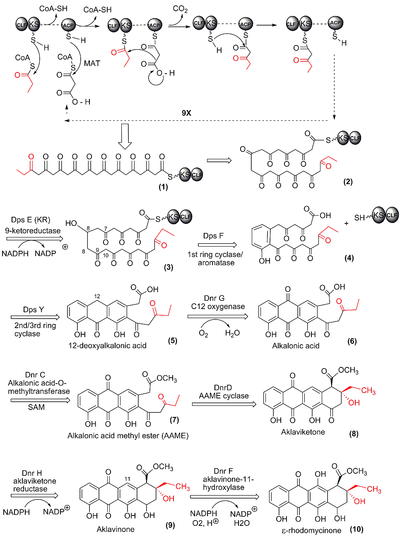
Streptomyces, yielded the medicines doxorubicin (Doxil), daunorubicin (DaunoXome), and streptozotocin (Zanosar). Doxorubicin is the precursor to valrubicin (Valstar), myocet, and pirarubicin. Daunorubicin is the precursor to idarubicin (Idamycin), epirubicin (Ellence), and zorubicin.
Streptomyces is the original source of dactinomycin (Cosmegen), bleomycin (Blenoxane), pingyangmycin (Bleomycin A5), mitomycin C (Mutamycin), rebeccamycin, staurosporine (precursor to stauprimide and midostaurin), neothramycin, aclarubicin, tomaymycin, sibiromycin, and mazethramycin.
Derivatives of Streptomycetes isolate migrastatin, including isomigrastatin, dorrigocin A & B, and the synthetic derivative macroketone, are being researched for anticancer activity.
Antibiotics
Most clinical antibiotics were found during the "golden age of antibiotics" (1940s–1960s). Actinomycin was the first antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces in 1940, followed by streptomycin three years later. Streptomycetes isolates (including various aminoglycosides) would go on to comprise over two-thirds of all marketed antibiotics.
Streptomyces antibiotics include:
- Chloramphenicol (Streptomyces venezuelae)[2]
- Daptomycin (Streptomyces roseosporus)[3]
- Fosfomycin (Streptomyces fradiae)[4]
- Lincomycin (Streptomyces lincolnensis)[5]
- Neomycin (Streptomyces fradiae)[6]
- Platensimycin (Streptomyces platensis)
- Puromycin (Streptomyces alboniger)[7]
- Streptomycin (Streptomyces griseus)[8]
- Tetracycline (Streptomyces rimosus and Streptomyces aureofaciens)[9]
Clavulanic acid (Streptomyces clavuligerus) is used in combination with some antibiotics (like amoxicillin) to weaken bacterial-resistance. Novel antiinfectives being developed include Guadinomine (Streptomyces sp. K01-0509),[10] an inhibitor of the type III secretion system.
Non-Streptomyces actinomycetes, filamentous fungi, and non-filamentous bacteria, have also yielded important antibiotics.
Antifungals
Nystatin (Streptomyces noursei), amphotericin B (Streptomyces nodosus), and natamycin (Streptomyces natalensis) are antifungals isolated from Streptomyces.
Immunosuppressants
Sirolimus (Rapamycin), ascomycin, and tacrolimus were isolated from Streptomyces. Pimecrolimus is a derivative of ascomycin. Ubenimex is derived from S. olivoreticuli.[11]
Antiparasitics
Streptomyces avermitilis synthesizes the antiparasitic ivermectin (Stromectol). Other antiparasitics made by Streptomyces include, milbemycin oxime, moxidectin, and milbemycin.
Biotechnology
Traditionally, Escherichia coli is the choice bacterium to express eukaryotic and recombinant genes. E. coli is well understood and has a successful track record producing insulin, the artemisinin precursor artemisinic acid, and filgrastim (Neupogen).[12][13] However, use of E. coli has limitations including misfolding of eukaryotic proteins, insolubility issues, deposition in inclusion bodies, [14] low secretion efficiency, secretion to periplasmic space.
Streptomyces offers potential advantages including superior secretion mechanisms, higher yields, a simpler end-product purification process, making Streptomyces an attractive alternative to E. coli and Bacillus subtilis.[14]
Streptomyces coelicolor, Streptomyces avermitilis, Streptomyces griseus, and Saccharopolyspora erythraea, are capable of secondary metabolite production. Streptomyces coelicolor has shown useful for the heterologous expression of proteins. Methods like "ribosome engineering" have been used to achieve 180-fold higher yields with S. coelicolor.[15]
Other
StreptomeDB, a directory of Streptomyces isolates, contains over 2400 compounds isolated from more than 1900 strains.[16][17] Streptomyces hygroscopicus and Streptomyces viridochromeogenes produce the herbicide bialaphos. Expansion of Streptomyces screenings have included endophytes, extremophiles, and marine varieties.
A recent screening of TCM extracts revealed a Streptomyces that produces a number of antitubercular pluramycins.[18]
See also
| Wikispecies has information related to: Streptomyces |
- Bacillus isolates
- Bacillus subtilis, a culinary/industrial bacterium used to produce a number of fermented soy products
- Biotechnology in pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Corynebacterium glutamicum, the industrial/pharmaceutical bacterium responsible for manufacturing a number of amino acids
- Erwinia chrysanthemi, a bacterium used to produce the chemotherapy medicine asparaginase
- Fungal isolates
- Medicinal molds
- Polyene antimycotics
- Sponge isolates
References
- ↑ Watve MG, Tickoo R, Jog MM, Bhole BD (November 2001). "How many antibiotics are produced by the genus Streptomyces?". Arch. Microbiol. 176 (5): 386–90. doi:10.1007/s002030100345. PMID 11702082.
- ↑ Akagawa, H.; Okanishi, M.; Umezawa, H. (1975). "A Plasmid Involved in Chloramphenicol Production in Streptomyces venezuelae: Evidence from Genetic Mapping". Journal of General Microbiology. 90 (2): 336–46. doi:10.1099/00221287-90-2-336. PMID 1194895.
- ↑ Miao, V. (2005). "Daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: Cloning and analysis of the gene cluster and revision of peptide stereochemistry". Microbiology. 151 (5): 1507–23. doi:10.1099/mic.0.27757-0. PMID 15870461.
- ↑ Woodyer RD, Shao Z, Thomas PM, et al. (November 2006). "Heterologous production of fosfomycin and identification of the minimal biosynthetic gene cluster". Chemistry & Biology. 13 (11): 1171–82. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2006.09.007. PMID 17113999.
- ↑ Peschke, Ursula; Schmidt, Heike; Zhang, Hui-Zhan; Piepersberg, Wolfgang (1995). "Molecular characterization of the lincomycin-production gene cluster of Streptomyces lincolnensis 78-11". Molecular Microbiology. 16 (6): 1137–56. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02338.x. PMID 8577249.
- ↑ Howard T. Dulmage (March 1953). "The Production of Neomycin by Streptomyces fradiae in Synthetic Media". Applied Microbiology. 1 (2): 103–106. PMC 1056872
 . PMID 13031516.
. PMID 13031516. - ↑ L. Sankaran & Burton M. Pogell (1975-12-01). "Biosynthesis of Puromycin in Streptomyces alboniger: Regulation and Properties of O-Demethylpuromycin O-Methyltransferase". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 8 (6): 721–32. doi:10.1128/AAC.8.6.721. PMC 429454
 . PMID 1211926. Retrieved 2012-01-19.
. PMID 1211926. Retrieved 2012-01-19. - ↑ Distler, Jürgen; Ebert, Andrea; Mansouri, Kambiz; Pissowotzki, Klaus; Stockmann, Michael; Piepersberg, Wolfgang (1987). "Gene cluster for streptomycin biosynthesis inStreptomyces griseus: Nucleotide sequence of three genes and analysis of transcriptional activity". Nucleic Acids Research. 15 (19): 8041–56. doi:10.1093/nar/15.19.8041. PMC 306325
 . PMID 3118332.
. PMID 3118332. - ↑ Dr. Mark Nelson; Robert A. Greenwald; Wolfgang Hillen; Mark L. Nelson (2001). Tetracyclines in biology, chemistry and medicine. Birkhäuser. pp. 8–. ISBN 978-3-7643-6282-9. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ↑ Holmes, TC; May, AE; Zaleta-Rivera, K; Ruby, JG; Skewes-Cox, P; Fischbach, MA; Derisi, JL; Iwatsuki, M; Ōmura, S; Khosla, C (2012). "Molecular insights into the biosynthesis of guadinomine: A type III secretion system inhibitor". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 134 (42): 17797–806. doi:10.1021/ja308622d. PMC 3483642
 . PMID 23030602.
. PMID 23030602. - ↑ Bauvois, B; Dauzonne, D (January 2006). "Aminopeptidase-N/CD13 (EC 3.4.11.2) inhibitors: Chemistry, biological evaluations, and therapeutic prospects". Medicinal Research Reviews. 26 (1): 88–130. doi:10.1002/med.20044. PMID 16216010.
- ↑ Brawner M, Poste G, Rosenberg M, Westpheling J (1991). "Streptomyces: a host for heterologous gene expression". Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2 (5): 674–81. doi:10.1016/0958-1669(91)90033-2. PMID 1367716.
- ↑ Payne G, DelaCruz N, Coppella S (1990). "Improved production of heterologous protein from Streptomyces lividans". Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 33 (4): 395–400. doi:10.1007/BF00176653. PMID 1369282.
- 1 2 Binnie C, Cossar J, Stewart D (1997). "Heterologous biopharmaceutical protein expression in Streptomyces". Trends Biotechnol. 15 (8): 315–20. doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(97)01062-7. PMID 9263479.
- ↑ Wang G, Hosaka T, Ochi K (2008). "Dramatic activation of antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor by cumulative drug resistance mutations.". Appl Environ Microbiol. 74 (9): 2834–40. doi:10.1128/AEM.02800-07. PMC 2394871
 . PMID 18310410.
. PMID 18310410. - ↑ Lucas X, Senger C, Erxleben A, Grüning BA, Döring K, Mosch J, et al. (2013). "StreptomeDB: a resource for natural compounds isolated from Streptomyces species.". Nucleic Acids Res. 41 (Database issue): D1130–6. doi:10.1093/nar/gks1253. PMC 3531085
 . PMID 23193280.
. PMID 23193280. - ↑
- ↑ Liu M, Abdel-Mageed WM, Ren B, He W, Huang P, Li X, et al. (2014). "Endophytic Streptomyces sp. Y3111 from traditional Chinese medicine produced antitubercular pluramycins.". Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 98 (3): 1077–85. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5335-6. PMID 24190497.
External links
- StreptomeDB
- Antibiotics and Streptomyces : the future of antibiotic discovery
- Bioprospecting for Microbial Endophytes and Their Natural Products - 2003