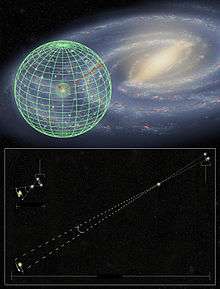
Stellar parallax
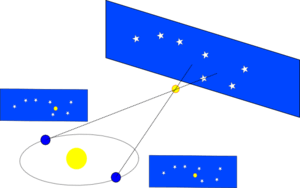
Stellar parallax is parallax on an interstellar scale: the apparent shift of position of any nearby star (or other object) against the background of distant objects. Created by the different orbital positions of Earth, the extremely small observed shift is largest at time intervals of about six months, when Earth arrives at exactly opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit, giving a baseline distance of about two astronomical units between observations. The parallax itself is considered to be half of this maximum, about equivalent to the observational shift that would occur due to the different positions of Earth and the Sun, a baseline of one astronomical unit (AU).
Stellar parallax is so difficult to detect that its existence was the subject of much debate in astronomy for thousands of years. It was first observed by Giuseppe Calandrelli who reported parallax in α-Lyrae in his work "Osservazione e riflessione sulla parallasse annua dall’alfa della Lira".[1] Then in 1838 Friedrich Bessel made the first successful parallax measurement ever, for the star 61 Cygni, using a Fraunhofer heliometer at Königsberg Observatory.[2][3]
Once a star's parallax is known, its distance from Earth can be computed trigonometrically. But the more distant an object is, the smaller its parallax. Even with 21st-century techniques in astrometry, the limits of accurate measurement make distances farther away than about 100 parsecs (roughly 326 light years) too approximate to be useful when obtained by this technique. Relatively close on a galactic scale, the applicability of stellar parallax leaves most astronomical distance measurements to be calculated by spectral red-shift or other methods.
Stellar parallax measures are given in the tiny units of arcseconds, or even in thousandths of arcseconds (milliarcseconds). The distance unit parsec is defined as the length of the leg of a right triangle adjacent to the angle of one arcsecond at one vertex, where the other leg is 1 AU long. Because stellar parallaxes and distances all involve such skinny right triangles, a convenient trigonometric approximation can be used to convert parallaxes (in arcseconds) to distance (in parsecs). The distance is simply the reciprocal of the parallax: For example, Proxima Centauri (the nearest star to Earth other than the Sun), whose parallax is 0.7687, is 1 / 0.7687 = 1.3009 parsecs (4.243 ly) distant.[4]
Early theory and attempts
Stellar parallax is so small (as to be unobservable until the 19th century) that its apparent absence was used as a scientific argument against heliocentrism during the early modern age. It is clear from Euclid's geometry that the effect would be undetectable if the stars were far enough away, but for various reasons such gigantic distances involved seemed entirely implausible: it was one of Tycho Brahe's principal objections to Copernican heliocentrism that in order for it to be compatible with the lack of observable stellar parallax, there would have to be an enormous and unlikely void between the orbit of Saturn and the eighth sphere (the fixed stars).[5]
James Bradley first tried to measure stellar parallaxes in 1729. The stellar movement proved too insignificant for his telescope, but he instead discovered the aberration of light,[6] the nutation of Earth’s axis, and catalogued 3222 stars.
19th and 20th centuries

Stellar parallax is most often measured using annual parallax, defined as the difference in position of a star as seen from Earth and Sun, i. e. the angle subtended at a star by the mean radius of Earth's orbit around the Sun. The parsec (3.26 light-years) is defined as the distance for which the annual parallax is 1 arcsecond. Annual parallax is normally measured by observing the position of a star at different times of the year as Earth moves through its orbit. Measurement of annual parallax was the first reliable way to determine the distances to the closest stars. The first successful measurements of stellar parallax were made by Friedrich Bessel in 1838 for the star 61 Cygni using a heliometer.[2][7]
Being very difficult to measure, only about 60 stellar parallaxes had been obtained by the end of the 19th century, mostly by use of the filar micrometer. Astrographs using astronomical photographic plates sped the process in the early 20th century. Automated plate-measuring machines[8] and more sophisticated computer technology of the 1960s allowed more efficient compilation of star catalogues. In the 1980s, charge-coupled devices (CCDs) replaced photographic plates and reduced optical uncertainties to one milliarcsecond.
Stellar parallax remains the standard for calibrating other measurement methods (see Cosmic distance ladder). Accurate calculations of distance based on stellar parallax require a measurement of the distance from Earth to the Sun, now based on radar reflection off the surfaces of planets.[9]
The angles involved in these calculations are very small and thus difficult to measure. The nearest star to the Sun (and also the star with the largest parallax), Proxima Centauri, has a parallax of 0.7687 ± 0.0003 arcsec.[4] This angle is approximately that subtended by an object 2 centimeters in diameter located 5.3 kilometers away.
Space astrometry for parallax
In 1989 the satellite Hipparcos was launched primarily for obtaining parallaxes and proper motions of nearby stars, increasing the reach of the method tenfold. Even so, Hipparcos is only able to measure parallax angles for stars up to about 1,600 light-years away, a little more than one percent of the diameter of the Milky Way Galaxy.
The European Space Agency's Gaia mission, launched 19 December 2013, is able to measure parallax angles to an accuracy of 10 microarcseconds, thus mapping nearby stars (and potentially planets) up to a distance of tens of thousands of light-years from Earth.[11]
The Hubble telescope WFC3 now has a precision of 20 to 40 microarcseconds, enabling reliable distance measurements up to 5,000 parsecs (20,000 ly).[12] This gives more accuracy to the Cosmic distance ladder and improves the knowledge of distances in the Universe, based on the dimensions of the Earth's orbit.
Other baselines
Secular parallax
The motion of the Sun through space provides a longer baseline that will increase the accuracy of parallax measurements, known as secular parallax. For stars in the Milky Way disk, this corresponds to a mean baseline of 4 AU per year, whereas for halo stars the baseline is 40 AU per year. After several decades, the baseline can be orders of magnitude greater than the Earth–Sun baseline used for traditional parallax. However, secular parallax introduces a higher level of uncertainty because the relative velocity of other stars is an additional unknown. When applied to samples of multiple stars, the uncertainty can be reduced; the precision is inversely proportional to the square root of the sample size.[13]
Other parallax in astronomy
Other uses of the term parallax in astronomy, with different meanings are the photometric parallax method, spectroscopic parallax, and dynamical parallax.
See also
- Cosmic distance ladder
- Moving cluster method
- Proper motion
- Apparent place
- Gaia (spacecraft), a mission collecting parallax data 2014-~2018
- TAU (spacecraft) (a space mission that would use parallax)
References
- ↑ Hockey, Thomas, ed. (2007). Biographical Encyclopedia of Astronomers. Springer-Verlag New York. ISBN 978-0-387-30400-7.
- 1 2 Zeilik & Gregory 1998, p. 44.
- ↑ Hirshfeld, Alan W (2002-05-01). Parallax. ISBN 978-0-8050-7133-7. Page 259.
- 1 2 Benedict, G. Fritz; Chappell; Nelan; Jefferys; Van Altena; Lee; Cornell; Shelus; Hemenway; Franz; Wasserman; Duncombe; Story; Whipple; Fredrick; et al. (1999). "Interferometric Astrometry of Proxima Centauri and Barnard's Star Using HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE Fine Guidance Sensor 3: Detection Limits for Substellar Companions". The Astronomical Journal. 118 (2): 1086–1100. arXiv:astro-ph/9905318
 . Bibcode:1999astro.ph..5318B. doi:10.1086/300975. Missing
. Bibcode:1999astro.ph..5318B. doi:10.1086/300975. Missing |last2=in Authors list (help) - ↑ See p.51 in The reception of Copernicus' heliocentric theory: proceedings of a symposium organized by the Nicolas Copernicus Committee of the International Union of the History and Philosophy of Science, Torun, Poland, 1973, ed. Jerzy Dobrzycki, International Union of the History and Philosophy of Science. Nicolas Copernicus Committee; ISBN 90-277-0311-6, ISBN 978-90-277-0311-8
- ↑ Buchheim, Robert (2007-10-04). The Sky is Your Laboratory. ISBN 978-0-387-73995-3. Page 184.
- ↑ Bessel, FW, "Bestimmung der Entfernung des 61sten Sterns des Schwans" (1838) Astronomische Nachrichten, vol. 16, pp. 65-96.
- ↑ CERN paper on plate measuring machine USNO StarScan
- ↑ Zeilik & Gregory 1998, § 22-3.
- ↑ "Hubble stretches the stellar tape measure ten times further". ESA/Hubble Images. Retrieved April 12, 2014.
- ↑ Henney, Paul J. "ESA's Gaia Mission to study stars". Astronomy Today. Retrieved 2008-03-08.
- ↑ Harrington, J.D.; Villard, Ray (10 April 2014). "NASA's Hubble Extends Stellar Tape Measure 10 Times Farther Into Space". NASA. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
Riess, Adam G.; Casertano, Stefano; Anderson, Jay; Mackenty, John; Filippenko, Alexei V. (2014). "Parallax Beyond a Kiloparsec from Spatially Scanning the Wide Field Camera 3 on the Hubble Space Telescope". arXiv:1401.0484v1
 [astro-ph.IM].
[astro-ph.IM]. - ↑ Popowski, Piotr; Gould, Andrew (1998-01-29). "Mathematics of Statistical Parallax and the Local Distance Scale". arXiv:astro-ph/9703140
 [astro-ph].
[astro-ph].
- Hirshfeld, Alan w. (2001). Parallax: The Race to Measure the Cosmos. New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-3711-6.
- Whipple, Fred L. (2007). Earth Moon and Planets. Read Books. ISBN 1-4067-6413-2..
- Zeilik, Michael A.; Gregory, Stephan A. (1998). Introductory Astronomy & Astrophysics (4th ed.). Saunders College Publishing. ISBN 0-03-006228-4..
Further reading
- Dyson, F. W. (1915). "Measurement of the distances of the stars". The Observatory. 38: 292. Bibcode:1915Obs....38..292D.