Police rank
Lists of the ranks of various police agencies and forces all around the world:
Australia
Generally, all police forces of Australia follow this rank structure with some individual state police forces have ranks differing slightly.
Insignia of rank displayed on epaulette in italics and brackets
For an overview of all distinct state and federal rank structures, see Australian police ranks.
- Commissioned Ranks
- Commissioner (two crossed and wreathed batons below a crown)
- Deputy Commissioner (two crossed and wreathed batons below a pip)
- Assistant Commissioner (two crossed batons)
- Commander (three pips in a triangular pattern below a crown)
- Chief Superintendent (two pips below a crown)
- Superintendent (one pip below a crown)
- Inspector (three pips)
- Senior Non-Commissioned Ranks
- Senior Sergeant (three chevrons, crown and surmounted by a laurel wreath)
- Sergeant (three chevrons)
- Non-Commissioned Ranks
- Senior Constable (two chevrons)
- Constable (plain epaulette)
- Probationary Constable (plain epaulette)
- Each state has its own distinct rank structure
- Australian Capital Territory
- Australian Federal Police
- New South Wales
- Northern Territory
- Queensland
- South Australia
- Tasmania
- Victoria
- Western Australia
Belgium
- Highest commissioned rank
- Hoofdcommissaris / commissaire divisionnaire (Chief Commissioner)
- Commissioned rank
- Commissaris / Commissaire (Commissioner)
- Senior non commissioned rank
- Hoofdinspecteur / Inspecteur principal (Chief Inspector/Superintendent)
- Non commissioned rank
- Inspecteur / Inspecteur (Inspector, equivalent to Constable or Officer)
- Auxiliary rank
- Agent van Politie / Agent de Police (Auxiliary Officer)
Bolivia
- Policia Egresado - Graduate Policeman
- Cabo - Corporal
- Sargento Segundo - Sergeant
- Sargento Primero - Staff sergeant
- Suboficial Segundo - Zone Sergeant
- Suboficial primero - Technical Sergeant
- Suboficial mayor - Station Sergeant
- Suboficial Supervisor - Sergeant Major
- Subteniente - Second Lieutenant
- Teniente - Lieutenant
- Capitan - Captain
- Mayor - Major
- Teniente Coronel - Lieutenant Colonel
- Coronel - Colonel
- General Director - Brigadier
- General Superior - Major General of Police
- General Supervisor - Lieutenant General of Police
- General Comandante - Director General of Police
Brazil
Brazil has several different police forces, each with its own ranks. At a federal level, there are the Federal Police (Portuguese: Polícia Federal, the equivalent to the FBI), the Federal Highway Police (Polícia Rodoviária Federal) and the Federal Railrway Police (Polícia Ferroviária Federal). At a state level, there are the Military Police (Polícia Militar, a gendarmerie type force not to be confused with the military polices of other countries, the Brazilian equivalent of which is the Army Police) and the Civil Police (Polícia Civil). At a city level, there is the Municipal Guard (Guarda Municipal). In terms of staff, the Military Police and the Civil Police are the most important ones, although in terms of headlines and prestige, the Federal Police is the one that concentrates most of the media attention.[1]
The Civil Police is responsible for investigating crimes whilst the Military Police is responsible for preventing them to take place, although it is not rare to see their functions clashing and ever so often they actually have open confronts.
The Civil Police is organized accordingly to functions. Scrivener (escrivão) is the lower rank position responsible for the internal work inside the police premises (e.g., collecting witness statements). Detective (detetive) or investigator (investigador) is the position responsible for actions outside the premises (e.g., investigating the circumstances of a crime). Delegate (delegado, similar to captain in USA) is the senior official (required to have a law degree) responsible for the lower ranks and for coordinating the whole work (investigations) of the Civil Police. The Civil Police also have the assistance of experts (peritos), which are the technical body. The Federal Police follows a very similar structure to the Civil Police, the same case in the Federal Highway and Railway polices.
The ranks listed below are valid for the state military police agencies (such as PMMG, PMESP, PMERJ and others) and are listed, respectively, from higher to lower ranks:
- coronel (colonel)
- tenente-coronel (lieutenant-colonel)
- major (major)
- capitão (captain)
- 1º tenente (1st lieutenant)
- 2º tenente (2nd lieutenant)
- aspirante-a-oficial (cadet, student rank)
- subtenente (under-lieutenant)
- 1º sargento (1st sergeant)
- 2º sargento (2nd sergeant)
- 3º sargento (3rd sergeant)
- cabo (corporal)
- soldado de 1ª classe (Private 1st Class)
- soldado de 2ª classe (Private 2nd Class, student rank)
The 2nd class soldier and the cadet are considered to be students in the formation courses and have no street policing duties (except in a very few cases, as probationary tours). Despite closely resembling the rank structure within the Brazilian army, there are no rank of general in the military police forces, as the Military Police is slotted under the Army control in case of war, with its colonels slotting under the Army generals.
Canada
Ranks of the Royal Canadian Mounted Police[2]:
- Commissioner
- Deputy Commissioner
- Assistant Commissioner
- Chief Superintendent
- Superintendent
- Inspector
- Corps Sergeant Major
- Sergeant Major
- Staff Sergeant Major
- Staff Sergeant
- Sergeant
- Corporal
- Police Constable 1st Class (Gendarme)
- Police Constable 2nd Class (Gendarme)
- Police Constable 3rd Class (Gendarme)
- Police Constable 4th Class (Gendarme)
- Cadet
Police Ranks for Provincial (With the exception of the Sûreté du Québec and Alberta Sheriffs) and the majority of Municipal Police Services as follows[3][4][5]:
- Chief of Police / Commissioner / Chief Constable
- Deputy Chief of Police / Deputy Chief Constable
- Staff Superintendent
- Superintendent
- Staff Inspector
- Inspector
- Sergeant Major
- Staff Sergeant
- Sergeant / Detective
- Police Constable 1st Class / Detective Constable
- Police Constable 2nd Class
- Police Constable 3rd Class
- Police Constable 4th Class
- Cadet
Police Ranks for the Alberta Sheriffs[6]:
- Chief
- Deputy Chief
- Superintendent
- Inspector
- Regimental Sergeant Major
- Sergeant
- Sheriff III
- Sheriff II
- Sheriff I
Ranks of the Sûreté du Québec[7]:
- Director General of the QPP (Directeur général)
- Deputy Director (Directeur adjoint)
- Chief Inspector (Inspecteur chef)
- Inspector (Inspecteur)
- Captain (Capitaine)
- Lieutenant (Lieutenant)
- Sergeant (5 classes of sergeants: Detective sgt, Staff sgt, specialist sgt)
- Agent (3 classes of Agents)
Ranks of the Service de police de la Ville de Montréal[8]:
- Directeur (Director)
- Associate Director
- Assistant Director
- Chief Inspector
- Inspector
- Commander
- Lieutenant / Detective Lieutenant
- Sergeant / Detective Sergeant
- Constable
Canadian Auxiliary Police Ranks as follows:
- Auxiliary Staff Superintendent
- Auxiliary Superintendent
- Auxiliary Staff Inspector
- Auxiliary Inspector
- Auxiliary Sergeant Major
- Auxiliary Staff Sergeant
- Auxiliary Sergeant
- Auxiliary Constable
Chile
These are the ranks used by Chilean police services.
POLICIA DE INVESTIGACIONES DE CHILE (PDI)
'Officers
- Director General
- Prefecto General
- Prefecto Inspector
- Prefecto
- Subprefecto
- Comisario
- Subcomisario
- Inspector
- Subinspector
- Detective
- Aspirante
CARABINEROS DE CHILE
Officers
- General Director
- General Inspector
- General
- Coronel
- Teniente Coronel
- Mayor
- Capitán
- Teniente
- Subteniente
Non-commissioned officers and enlisted
- Suboficial Mayor
- Suboficial
- Sargento 1º
- Sargento 2º
- Cabo 1º
- Cabo 2º
- Carabinero
China
Chinese Police Officers under the Ministry of Public Security use rank insignia on both side of shoulders in the duty uniform. Senior officers ranking at Commissioner and Superintendent levels wear these on the white collar uniform, and for Inspector level and below officers wear them on the sky blue collar uniform.
Senior Officers
- Commissioner of Police (Chinese: 总警监, zǒng jǐngjiān)
Mr GUO Sheng-kun, currently Commissioner of Police, Minister of Public Security(since December 2012). Shoulder insignia: national coat of arms fully circled with a pair of olive branch.
- Deputy Commissioner of Police (副总警监, fù zǒng jǐngjiān)
Deputy Minister of Public Security, shoulder insignia: national coat of arms partly circled with a pair of olive branch.
- Superintendent 1st Class (一级警监, yījí jǐngjiān)
Assistant Commissioner of Police is also wearing this rank, SUPT 1st class normally commands a functional bureau (e.g. CID, Immigration, Traffic, Anti-Smuggling) or a province formation, direct report to DCP. Shoulder insignia: three pips with olive leaves.
- Superintendent 2nd Class (二级警监, èrjí jǐngjiān)
Normally is second in charge of a functional bureau, or a province formation, or a city police headquarters commander. Shoulder insignia: two pips with olive leaves.
- Superintendent 3rd Class (三级警监, sānjí jǐngjiān)
Normally commands police division of a functional bureau, or the head of a police sub-bureau of a city. Shoulder insignia: one pip with olive leaves.
- Inspector 1st Class (一级警督, yījí jǐngdū)Shoulder insignia: three pips with two silver bars.
- Inspector 2nd Class (二级警督, èrjí jǐngdū)Shoulder insignia: two pips with two silver bars.
- Inspector 3rd Class (三级警督, sānjí jǐngdū)Shoulder insignia: one pip with two silver bars.
Administrative positions do not exactly tally with ranks among Inspector level and junior officers, admin positions (from PC to Station Commander or even Deputy Chief of a sub-Bureau), are various and flexible, it depends on each individual's qualifications and multiple skills, performance efficiency and effectiveness, years of service, personality and communication ability, potential leadership. Loyal and qualified officers with no misconduct record, are eligible to get rank promotion at every four-year of service (only applicable from Sgt 1st class to Insp 1st class). Which means for example, for a normal PC holding a non-commissioned position during his/her entire police career, with the increasing years of service, the highest rank he/she may attain is either Insp 3rd class (for high school and below qualification holders), or Insp 1st class (for university graduated certificate holders). Alternatively, young officers who are holding university degree(regardless of disciplines and majors), usually after three years of service, once his/her overall performance and ability meet operation needs, recommended by his/her team leader or a higher ccommanding officer, may have chance to get promoted (as sub-unit commander, detective supervisor... ).
Officers at this mid-rank level play very important roles as the "Cornerstone" of the national police force. As most of them have already served quite long years, with accumulated work experiences, no matter standing at commanding or non-commanding position, they are either undertaking major responsibilities in public security or nurturing young officers with self model behaviours and proper instructions.
Junior Officers
- Sergeant 1st Class (一级警司, yījí jǐngsī)Shoulder insignia: three pips with one silver bar. Highest admin position at this rank can be Station Commander, or Operations Squad Leader and sub-Unit Commander/Section Head at a police bureau or sub-bureau, normally in charge of a detective case or a common police raid operation.
- Sergeant 2nd Class (二级警司, èrjí jǐngsī)Shoulder insignia: two pips with one silver bar. University degree holder's entry ranking level is Sgt 2 class. Other than basic duties, also attend and assist sub-unit commander/section head in handling all kinds of cases. Sometimes is second in charge or Acting Commander during a case or operation.
- Sergeant 3rd Class (三级警司, sānjí jǐngsī)Shoulder insignia: one pip with one silver bar. Other than basic duties, also attend and assist sub-unit commander/section head in handling all kinds of cases.
- Police Constable 1st Class (一级警員, yījí jǐngyuán)Shoulder insignia: two pips. Perform road patrol and vehicle command duties.
- Police Constable 2nd Class (二级警員, èrjí jǐngyuán)Shoulder insignia: one pip. Perform road patrol and vehicle command duties.
Loyal and qualified officers with no misconduct record, are eligible to attain rank promotion at every three-year of service (only applicable from PC 2nd class to Sgt 1st class). Rank does not have any connection with position, it can only shows how many years you have been work for police unit.
- Probationary Police Constable 见习警员 Shoulder insignia: two stripes.(Normally one year probationary period) Might be attaching to any of police stations or sub-units to familiar with the real police operations.
- Cadet (at PTS-Police Training School) 学警 Shoulder insignia: one stripe.
The People's Armed Police, as part of the People's Liberation Army, uses the same ranks and uniform as the PLA itself, save for the China Coast Guard which uses navy-style ranks and uniform plus the China Maritime Safety Administration.
Croatia
Regular Police ranks
- Police Director (Ravnatelj policije)
- Deputy Police Director (Zamjenik ravnatelja policije)
- Major Police advisor (Glavni policijski savjetnik)
- Police advisor (Policijski savjetnik)
- Major Police inspector (Glavni policijski inspektor)
- Independent Police inspector (Samostalni policijski inspektor)
- Upper Police inspector (Viši policijski inspektor)
- Police inspector (Policijski inspektor)
- Independent Police sergeant (Samostalni policijski narednik)
- Upper Police sergeant (Viši policijski narednik)
- Police sergeant (Policijski narednik)
- Independent Police officer (Samostalni policajac)
- Upper Police officer (Viši policajac)
- Police officer (Policajac)
- Probationer with college (Vježbenik više i visoke stručne spreme)
- Probationer with secondary school (Vježbenik Srednje Stručne Spreme)
Special Intervention Police ranks
- Commander of intervention Police (Zapovjednik interventne policije)
- Deputy of commander of intervention Police (Pomoćnik zapovjednika interventne policije)
- Instructor in headquarters of intervention Police (Instruktor u zapovjedništvu interventne policije)
- Commander of intervention Police unit (Zapovjednik jedinice interventne policije)
- Deputy of commander of intervention Police unit (Zamjenik zapovjednika jedinice interventne policije)
- Commander of troop in intervention Police (Zapovjednik satnije)
- Deputy of commander of troop in intervention Police (Pomoćnik zapovjednika satnije)
- Commander of platoon in intervention Police - instructor (Zapovjednik voda- instruktor)
- Commander of section in intervention Police(Zapovjednik odjeljenja)
- Leader of intervention group (Vođa interventne grupe)
- Police officer in intervention group (Interventni policajac)
Cyprus
| Title | Title in Greek |
|---|---|
| Chief of Police | Αρχηγός |
| Deputy Chief of Police | Υπαρχηγός |
| Assistant Chief of Police | Βοηθός Αρχηγός |
| Chief Superintendent | Ανώτερος Αστυνόμος |
| Superintendent A' | Αστυνόμος Α' |
| Superintendent B' | Αστυνόμος Β' |
| Chief Inspector | Ανώτερος Υπαστυνόμος |
| Inspector | Υπαστυνόμος |
| Senior Sergeant | Αρχιλοχίας |
| Sergeant | Λοχίας |
| Acting Sergeant Senior Constable |
Αναπληρωτής Λοχίας Αρχιαστυφύλακας |
| Acting Sergeant | Αναπληρωτής Λοχίας |
| Senior Constable | Αρχιαστυφύλακας |
| Constable | Αστυφύλακας |
| Special Constable | Ειδικός Αστυφύλακας |
Denmark
| |
Insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rank | Rigspolitichefen | Politidirektør, Vicepolitidirektør, Vicerigspolitichef or Politimester | Chefpolitiinspektør or Chefanklager | Vicepolitimester, Chefanklager, Politiinspektør or Chefpolitiinspektør | Vicepolitiinspektør | Politikommissær | Politiassistent af 1. grad | Politiassistent af 2. grad | Politibetjent | |
| EN Rank | National Police Commissioner | Chief of Police, | Chief Inspector, Chief Prosecutor | Deputy Chief of Police, Inspector, Chief Inspector | Deputy Inspector | Commissioner | Police Constable First Class | Police Constable | Policeofficer | |
Estonia
- General (Politseikindral)
- Inspector-General (Politseikindralinspektor)
- Colonel (Politseikolonel)
- Lieutenant Colonel (Politseikolonelleitnant)
- Major (Politseimajor)
- Captain (Politseikapten)
- Lieutenant (Politseileitnant)
- Senior Comissar (Vanemkomissar)
- Comissar (Komissar)
- Chief Constable, Chief Inspector (Ülemkonstaabel, üleminspektor)
- Senior Constable, Senior Inspector (Vanemkonstaabel, vaneminspektor)
- Constable, Inspector (Konstaabel, inspektor)
- Junior Constable, Junior Inspector (Nooremkonstaabel, nooreminspektor)
Finland
- National Police Commissioner (poliisiylijohtaja)
- Deputy National Police Commissioner (poliisijohtaja)
- Chief Superintendent (poliisitarkastaja)
- Police chief (poliisipäällikkö)
- Deputy Police Chief (apulaispoliisipäällikkö)
- Superintendent (ylikomisario)
- Chief Inspector (komisario)
- Sergeant (ylikonstaapeli)
- Senior Constable (vanhempi konstaapeli)
- Constable (nuorempi konstaapeli)
France
Police Nationale
Corps de Conception et de Direction
- Director of Active Services (Directeur des Services Actifs)
- Inspector General (Inspecteur Général)
- Controller General (Contrôleur Général)
- Divisional Commissioner (Commissaire Divisionnaire)
- Commissioner (Commissaire de Police)
Corps de Commandement
- Police Major (Commandant de Police)
- Police Captain (Capitaine de Police)
- Police Lieutenant (Lieutenant de Police)
- Intern Police Lieutenant (Lieutenant de Police stagiaire)
- Student Police Lieutenant (élève Lieutenant de Police)
Corps d'Encadrement et d'Application
- Police (Sergeant) Major (Major de police)
- Police Chief Brigadier (Brigadier-chef de police)
- Police Brigadier Brigadier de police
- Peace Guard (Gardien de la Paix)
- Intern Peace Guard (Gardien de la Paix stagiaire)
- Student Peace Guard (élève Gardien de la Paix)
Gendarmerie
Office(CO)
- Army General (Five Stars) (Général d'armée)
- Army Corp General (Four Stars) (Général de corps d'armée)
- Division General (Three Stars) (Général de division)
- Brigade General (Two Stars) (Général de brigade)
- Colonel (Colonel)
- Lieutenant-Colonel (Lieutenant-Colonel)
- Major (Commandant)
- Captain (Capitaine)
- Lieutenant (Lieutenant)
- Student Lieutenant (Elève Officier)
Sub-Officers[NCO]
- Master Sergeant (Major)
- Sergeant First Class (Adjudant-chef)
- Staff Sergeant (Adjudant)
- Chief Deputy (Maréchal des logis chef)
- Deputy (Gendarme de carrière )
- Probationary Deputy (Gendarme sous contrat)
- Student Deputy (Elève Gendarme)
Volunteers (5 years)
- Volunteer Lieutenant (AGIV, or Aspirant de Gendarmerie Issu du Volontariat)
- Senior Volunteer Assistant Deputy (Maréchal des logis)
- Chief Volunteer Assistant Deputy (Brigadier-chef)
- First Class Volunteer Assistant Deputy (Brigadier)
- Volunteer Assistant Deputy (Gendarme Adjoint Volontaire)
Germany
The following ranks are in use by state police forces. Detective Ranks follow the same scheme, replacing the word Polizei with Kriminal, for example a plainclothed detective lieutenant is called Kriminalkommissar. The Federal Police of Germany basically follows the scheme, but deviates in the flag ranks.
Politically appointed
They are comparable to military flag (General) officers, and are appointed by the state Minister of Interior (Senators of Interior in City-States). For federal agencies the federal Minister of Interior is responsible. They are usually specialists in public administration and have a master-level law degree. Since they are outside of the career system, they receive payment according to the B-scale of public officer payment grades.
- President of the Federal Police Commission (Präsident des Bundespolizeipräsidiums), the highest police rank, only used by the Federal Police, responsible to the federal Ministry of Interior
- President of Police (Polizeipräsident), commands an independent regional authority of state police (Polizeipräsidium, Landespolizeidirektion, or similar), directly subordinated to the corresponding state ministry of interior.
- Vice President of Police (Polizeivizepräsident or Vizepräsident), also used in some states, serves as assistant to the state police commander
- Inspector of/Director of (stand-by) police (Inspekteur/Direktor der Bereitschaftspolizei), this rank is named differently in some states. The officer commands the stand-by police forces of the state.
Higher echelon
Comparable to military staff officers, Major and above. The ranks are available for applicants who completed master level university studies, usually in law. It is possible for officers from the elevated echelon to obtain a master degree from the Deutsche Hochschule der Polizei, so they can enter higher ranks.
- Police Chief Director (Leitender Polizeidirektor) acts as lieutenant to the President of Police or heading a branch service of state police. As a career position it corresponds to grade A16. Four gold stars on shoulder patch.
- Police Director (Polizeidirektor), commands a subdivision of a regional authority of state police, either territorial (encompassing roughly one or two Districts of Germany districts) or by branches (traffic, crime). Grade A15. 3 gold stars.
- Police Senior Councillor (Polizeioberrat), grade A14. 2 gold stars.
- Police Councillor (Polizeirat), commands a local police division (Polizeiinspektion) or special branch; grade A13. 1 gold star.
Elevated echelon
Comparable to military officers, Lieutenant and above. The ranks are obtained after receiving a bachelor level degree of a state college of public administration. In several states of Germany this is the lowest echelon for service entry, the medium service echelon is being abolished.
- First Police Chief Inspector (Erster Polizeihauptkommissar), may serve in lieu of a Police Councillor, grade A13. 4 silver stars (in some states 5).
- Police Chief Inspector (Polizeihauptkommissar), grades A11 and A12. 3 silver stars, in some states 4 stars when in grade A12.
- Police Senior Inspector (Polizeioberkommissar), grade A10, 2 silver stars.
- Police Inspector (Polizeikommissar), grade A9, 1 silver star.
Medium echelon
Comparable to military non-commissioned officers. Those ranks are usually obtained during or after two years service in training companies (Ausbildungshundertschaften) of the Bereitschaftspolizei. The ranks are indicated by light blue (with blue uniform) or light green (with green-brown uniform) stars.
- Police Chief Master (upgraded pay) (Polizeihauptmeister mit Amtszulage), may serve in lieu of a Police Inspector, grade A9 with upgrade, 4 or 5 stars.
- Police Chief Master (Polizeihauptmeister), grade A9, 4 stars.
- Police Senior Master (Polizeiobermeister), grade A8, 3 stars.
- Police Master (Polizeimeister), grade A7, 2 stars.
- Chief Constable (Hauptwachtmeister), grade A6, 1 star (only in a few states, usually during service in the Bereitschaftspolizei).
- Senior Constable (Oberwachtmeister) (only in a few states, usually during service in the Bereitschaftspolizei), grade A5.
There have been lower ranks in use in earlier times, with the abolishment of the basic echelon, they have been out of use since the 1980s. The most well-known of these is Wachtmeister (Constable) which still is considered the standard address for a policeman of unknown rank, even though it may now be considered condescending, given the policeman has a higher rank than mere Wachtmeister.
Pre-commission
- Candidates (Anwärter), usually the word is appended to the rank, to which the person is going to be commissioned, e.g. Polizeikommissaranwärter. Pay is a reduced amount of the corresponding rank.
Hong Kong
- Commissioner of Police (CP)
- Deputy Commissioner of Police (DCP)
- Senior Assistant Commissioner of Police (SACP)
- Assistant Commissioner of Police (ACP)
- Chief Superintendent of Police (CSP)
- Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP)
- Superintendent of Police (SP)
- Chief Inspector of Police (CIP)
- Senior Inspector of Police (SIP)
- Inspector of Police (IP)
- Probationary Inspector of Police (PI)
- Station Sergeant (SSGT)
- Sergeant (SGT)
- Senior Police Constable (SPC)
- Constable (PC)
Iceland
| Rank | Title | Icelandic title |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | National Commissioner | Ríkislögreglustjóri |
| 2 | Deputy National Commissioner | Vararíkislögreglustjóri |
| Police Commissioner | Lögreglustjóri | |
| Director of the Police College | Skólastjóri Lögregluskóla ríkisins | |
| 3 | Deputy Commissioner | Varalögreglustjóri í Reykjavík |
| Staðgengill lögreglustjóra | ||
| 4 | Chief Superintendent/Detective Chief Superintendent | Yfirlögregluþjónn |
| 5 | Superintendent/Detective Superintendent | Aðstoðaryfirlögregluþjónn |
| 6 | Chief Inspector | Aðalvarðstjóri |
| Detective Chief Inspector | Lögreglufulltrúi | |
| 7 | Inspector | Varðstjóri |
| Detective Inspector | Rannsóknarlögreglumaður | |
| 8 | Brevet Inspector | Staðgengill Varðstjóra |
| 9 | Policeman/Constable | Lögreglumaður |
| 10 | Trainee | Lögreglunemi |
| Temporarily Employed Policeman | Afleysingamaður í lögreglu | |
| Reservist | Héraðslögreglumaður |
India
Main Articles : List of Police Ranks in India and Indian Police Service (I.P.S.)
Gazetted officers include all the Indian Police Service officers and all State Police Services officers of and above the rank of Assistant Commissioner of Police (ACP) or Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP) in State Police and Metropolitan Police forces respectively.
Ranks of Gazetted Officers
- Director Intelligence Bureau (post held by senior most Indian Police Service officer; not a rank)
- Commissioner of Police (State) or Director General of Police
- Special Commissioner of Police or Additional Director General of Police
- Joint Commissioner of Police or Inspector General of Police
- Additional Commissioner of Police or Deputy Inspector General of Police
- Deputy Commissioner of Police or Senior Superintendent of Police or Senior Commandant
- Deputy Commissioner of Police or Superintendent of Police or Commandant
- Additional Deputy Commissioner of Police or Additional Superintendent of Police or Deputy Commandant
- Assistant Commissioner of Police or Deputy Superintendent of Police or Assistant Commandant
- Assistant Superintendent of Police (IPS Probationary Rank: 2 years of service)
- Assistant Superintendent of Police (IPS Probationary Rank: 1 year of service)
Ranks of non-Gazetted Officer
- Sub-Inspector (S.I.)
- Assistant Sub Inspector (A.S.I.)
- Head Constable
- Senior Constable
- Constable
Indonesia
Indonesian Police Ranks:
| Worn on: | High Ranking officers | Middle Ranking officers | First Ranking officers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceremonial Uniform (PDU) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Service Uniform (PDH) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Field Uniform (PDL) on collar |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rank: | Police General | General Commissioner | General Inspector | Brigadier General | Police Chief commissioner | Police superintendent | Police Commissioner | Chief Inspector | First Inspector | Second Inspector |
| Worn on: | Asst. Inspector | Brigadiers (NCO/Constable) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceremonial Uniform (PDU) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Service Uniform (PDH) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Field Uniform (PDL) on collar |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rank: | Sub-inspector | Second sub-inspector |
Chief Brigadier |
Brigadier | First Brigadier |
Second Brigadier |
- The Ranks below is only used in the Mobile Brigade and Water police units:
| Worn on: | Enlisted | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceremonial Uniform (PDU) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Service Uniform (PDH) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Field Uniform (PDL) on collar |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rank: | Brigadier Adjutant |
First Brigadier Adjutant |
Second Brigadier Adjutant |
Chief Agent |
First Agent |
Second Agent |
Islamic Republic of Iran
Police Commissioned Officers and Enlisted Ranks

| Commissioned Officer rank insignia of the Islamic Republic of Iran Police (NAJA) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Police General | Police Lieutenant General | Police Major General | Police Brigadier General | Police Second Brigadier General | Police Colonel | Police Lieutenant Colonel | Police Major | Police Captain | Police First Lieutenant | Police Second Lieutenant | Police Third Lieutenant |
| Persian: ارتشبد | Persian: سپهبد | Persian: سرلشکر | Persian: سرتیپ | Persian: سرتیپ دوم | Persian: سرهنگ | Persian: سرهنگ دوم | Persian: سرگرد | Persian: سروان | Persian: ستوان یکم | Persian: ستوان دوم | Persian: ستوان سوم |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Enlisted rank insignia of the Islamic Republic of Iran Police (NAJA) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Command Sergeant Major | Sergeant Major(Staff) | Sergeant First Class/First Sergeant | Staff Sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Lance Corporal | Senior Policeman | Policeman | |||
| Persian: استوار یکم | Persian: استوار دوم | Persian: گروهبان یکم | Persian: گروهبان دوم | Persian: گروهبان سوم | Persian: سرجوخه | Persian: سرباز یکم | Persian: سرباز دوم | Persian: سرباز | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||
Iraq
The Iraqi Police is made up of three branches, under the command of the Iraqi Ministry of Interior, these being the Iraqi Police Service which tasked with general patrol of Iraq's cities, the National Police which are a paramilitary organisation which deals with incidents that are beyond the control of the Iraqi Police, but are not so serious the Iraqi Army are involved, and the supporting force that is made up of the Department of Border Enforcement.[9]
Iraqi Police Service ranks, ordered lowest to highest with symbol on epaulette:[10]
- Chief of Police/رئيس الشرطة - (single bar, Crossed wreath & Star)
- Chief Superintendent/مشرفة رئيسيّة - (Crossed wreath & Star)
- Superintendent/مشرفة - (Three stars)
- Chief Inspector/[شف ينسبكتور] - (Bar, and two stars)
- Inspector/مفتشة - (Bar, and one star)
- Captain/نقيب - (Two stars)
- Lieutenant/ملازم أوّل - (One star)
- Sergeant/رقيب - (Four bars)
- Patrolman/[بترولمن] - (One bar)
Italy
See Italian State Police Ranks
Ireland
Ranks of the Garda Síochána (Guardians of the Peace) the Police service of the Republic of Ireland.
- Garda Commissioner
- Deputy Commissioner
- Assistant Commissioner
- Chief Superintendent
- Superintendent
- Inspector
- Sergeant
- Garda (equivalent to constable or police officer)
Japan
- Commissioner General (Japanese: 警察庁長官 Keisatsu-chō Chōkan): The Chief of National Police Agency. The rank outside. 1 capacity.
- Superintendent General (警視総監 Keishi-sōkan): The Chief of Metropolitan Police Department. 1 capacity.
- Senior Commissioner (警視監 Keishi-kan): Deputy Commissioner General, Deputy Superintendent General, The Chief of Regional Police Bureau, The Chief of Prefectural Police Headquarters, others. 38 capacity.
- Commissioner (警視長 Keishi-chō): The Chief of Prefectural Police Headquarters.
- Assistant Commissioner (警視正 Keishi-sei): The Chief of Police Station(large). National Police Agency officers occupy the higher ranks above it.
- Superintendent (警視 Keishi): The Chief of Police Station(small or middle), The Vice Commanding Officer of Police Station, Commander of Riot Unit.
- Police Chief Inspector (警部 Keibu): Squad Commander of Police Station, Leader of Riot Company.
- Inspector (警部補 Keibu-ho):Squad Sub-Commander of Police Station, Leader of Riot Platoon. National Police Officer 1st class's career start from this rank.
- Sergeant (巡査部長 Junsa-buchō):Field supervisor, Leader of Police box. National Police Officer 2nd class's career start from this rank.
- Senior Police Officer (巡査長 Junsa-chō): Honorary rank of Police Officer.
- Police officer, (巡査 Junsa):Prefectural Police Officer's career start from this rank.
South Korea
- Commissioner General (치안총감, 治安總監): at most one may be appointed at a time.
- Chief Superintendent General (치안정감, 治安正監): at most five may be appointed at a time.
- Senior Superintendent General (치안감, 治安監)
- Superintendent General (경무관, 警務官)
- Senior Superintendent (총경, 總警)
- Superintendent (경정, 警正)
- Senior Inspector (경감, 警監)
- Inspector (경위, 警衛)
- Assistant Inspector (경사, 警査)
- Senior Police Officer (경장, 警長)
- Police Officer (순경, 巡警)
- Newly commissioned officers are appointed as Policeman Assistant (순경시보, 巡警試補) for a two-year probationary period. The uniform and insignia of an assistant is identical to those of a Policeman.
- Auxiliary Policeman (의경, 義警)
- Sergeant Constable (수경, 首警)
- Corporal Constable (상경, 上警)
- Private Constable First Class (일경, 一警)
- Private Constable (이경, 二警)
Latvia
- Ģenerālis/Police general
- Pulkvedis/Colonel
- Pulkvežleitnants/Lieutenant Colonel
- Majors/Major
- Kapteinis/Captain
- Virsleitnants/First lieutenant
- Leitnants/Lieutenant
- Virsnieka vietnieks/Warrant Officer
- Virsseržants/First sergeant
- Seržants/Sergeant
- Kaprālis/Corporal
- Kursants
- Ierindnieks/Private
Lithuania
Generalinis komisaras/Comissionier-General
A class officers
- Vyriausiasis komisaras/Chief Commissioner
- Vyresnysis komisaras/Senior commissioner
- Komisaras/Commissioner
B class officers
- Komisaras inspektorius/Comissionier inspector
- Vyresnysis inspektorius/Chief inspector
- Inspektorius/Inspector
C class officers
- Viršila/Sergeant
- Vyresnysis policininkas/Police officer 1st class
- Policininkas/Police officer
- Jaunesnysis policininkas/Junior police officer
Luxembourg
The Grand Ducal Police of Luxembourg has the following ranks (from top to bottom):
- Director General (directeur général)
- Assistant Director General (directeur général adjoint)
- First Division Commissioner (1er commissaire divisionnaire)
- Division Commissioner (commissaire divisionnaire)
- Assistant Division Commissioner (commissaire divisionnaire adjoint)
- First Senior Commissioner (1er commissaire principal)
- Senior Commissioner (commissaire principal)
- Chief Commissioner (commissaire en chef)
- Commissioner (commissaire)
- Chief Inspector (inspecteur-chef)
- First Inspector (premier inspecteur)
- Inspector (inspecteur)
- Assistant Inspector (inspecteur adjoint)
- Chief Brigadier (brigadier-chef)
- Senior Brigadier (brigadier principal)
- First Brigadier (premier brigadier)
- Brigadier (brigadier)
Macau
The Public Security Police Force of Macau (CPSP) includes the following categories, ranks and respective main functions :[11]
- Senior ranks
- Superintendent general (Portuguese: superintendente-geral): commander of the CPSP,
- Superintendent (superintendente): deputy commander of the CPSP,
- Intendent (intendente): commanding officer of level I units,
- Sub-Intendent (subintendente): commanding officer of level II units,
- Commissioner (comissário): commanding officer of level III units,
- Sub-commissioner (subcomissário): commanding officer of level IV units,
- Chief (chefe): commanding officer of level V units,
- Sub-chief (subchefe): coordinator of complex tasks;
- Basic ranks
- Principal constable (guarda principal): coordinator of simple tasks,
- Constable first class (guarda de primeira): executor of operational, technical or administrative tasks,
- Constable (guarda): executor of operational, technical or administrative tasks.
Malaysia
Below shown are the rank structure of the Royal Malaysian Police.
- Inspector General Grade
- Inspector General of Police [IGP]: National Chief Police.
- Deputy Inspector General of Police [DIG]: Deputy National Chief Police.
- Commissioner of Police [CP] Department Chief Police
- Senior Deputy Commissioner of Police
- Deputy Commissioner of Police [DCP] : State Chief Police Officer [CPO]
- Senior Assistant Commissioner of Police
- Assistant Commissioner of Police [ACP]: District Chief Police.
- Superintendent Grade
- Superintendent of Police [SUPT]
- Deputy Superintendent of Police [DSP]: District Division Chief
- Assistant Superintendent of Police [ASP]: Station Chief Police.
Inspector Grade
- Inspector [INSP]
- Probationary Inspector [P/INSP]
- Enlisted Grade
- Sub-Inspector [S/INSP]
- Sergeant Major [SM]
- Sergeant [SGT]
- Corporal [CPL]
- Lance Corporal [L/CPL]
- Constable
Netherlands
| Rank | First Chief Commissioner (Eerste Hoofdcommissaris) |
Chief Commissioner (Hoofdcommissaris) |
Chief Superintendent (Commissaris) |
Superintendent (Hoofdinspecteur) |
Inspector (Inspecteur) |
Sergeant (Brigadier) |
| Shoulder | ||||||
| Sleeve |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Rank | Senior Constable (Hoofdagent) |
Constable (Agent) |
Police Patrol Officer (Surveillant) |
Police Trainee (Aspirant) |
Non Executive Employee (Niet-Executieve Medewerker) | |
| Shoulder | ||||||
| Sleeve |  |  |  |  |  |
Norway
| Norwegian | Politidirektør | Assisterende politidirektør |
Politimester | Visepolitimester | Politiinspektør og Politiadvokat |
Politiadvokat | Politifullmektig |
| Rank | National Police Commissioner |
Assistant National Commissioner |
Chief of Police | Deputy Chief of Police |
Assistant Chief of Police |
Police Prosecutor |
Junior Police Prosecutor |
| Insignia |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Norwegian | Politistasjonssjef og Lensmann |
Politioverbetjent | Politiførstebetjent | Politibetjent 3 | Politibetjent 2 | Politibetjent 1 | Politi reserven |
| Rank | Police Chief Superintendent |
Police Superintendent |
Police Chief Inspector |
Police Inspector | Police Sergeant | Police Constable | Police Reserve |
| Insignia |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
Source: Norwegian National Police[12]
Pakistan Rangers
The following ranks are observed in the top para-military force of Pakistan
Commissioned officers
- Director General (DG) - Equivalent to Major General
- Deputy Director General (DDG) - Equivalent to Brigadier
- Senior Superintendent Rangers(SSR) - Equivalent to Lieutenant Colonel
- Superintendent Rangers(SR) - Equivalent to Major
- Deputy Superintendent Rangers (DSR) - Equivalent to Captain
Philippines
The following ranks are observed in the PNP as of 2009 with the following:[13]
Commissioned officers
- Director General - General
- Deputy Director General (DDG) - Lieutenant General
- Director (Dir.) - Major General
- Chief Superintendent (C/Supt.) - Brigadier General
- Senior Superintendent (S/Supt.) - Colonel
- Superintendent (Supt.) - Lieutenant Colonel
- Chief Inspector (C/Insp.) - Major
- Senior Inspector (S/Insp.) - Captain
- Inspector (Insp.) - Lieutenant
Note: Rank in Italics is the Army equivalent. There is no Second Lieutenant rank-equivalent in the PNP.
Non-commissioned officers
- Senior Police Officer IV (SPO4) - Senior Master Sergeant / Chief Master Sergeant
- Senior Police Officer III (SPO3) - Master Sergeant
- Senior Police Officer II (SPO2) - Technical Sergeant
- Senior Police Officer I (SPO1) - Staff Sergeant
- Police Officer IV (PO4) - Sergeant at Arms
- Police Officer III (PO3) - Sergeant
- Police Officer II (PO2) - Corporal
- Police Officer I (PO1) - Private First Class
Note: Rank in Italics is the Army equivalent. There is no Private rank-equivalent in the PNP.
Poland
| Group | Generals | Senior Officers | Junior Officers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polish | generalny inspektor Policji | nadinspektor | inspektor | młodszy inspektor |
podinspektor | nadkomisarz | komisarz | podkomisarz | |
| Rank | Inspector General of Police |
Chief Inspector |
Inspector | Junior Inspector |
Deputy Inspector |
Chief Commissioner |
Commissioner | Deputy Commissioner | |
| Insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
| Group | Aspirants | Non-commissioned Officers | Constables | ||||||
| Polish | aspirant sztabowy | starszy aspirant | aspirant | młodszy aspirant | sierżant sztabowy | starszy sierżant | sierżant | starszy posterunkowy | posterunkowy |
| Rank | Staff Aspirant |
Senior Aspirant |
Aspirant | Junior Aspirant |
Staff Sergeant |
Senior Sergeant |
Sergeant | Senior Constable | Constable |
| Insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
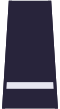 |
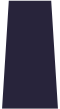 |
Portugal
The Public Security Police (PSP) of Portugal includes the following categories, ranks, insignia and respective main functions:
- Police Officers
-
 National Chief Superintendent: National Director of the PSP,
National Chief Superintendent: National Director of the PSP, -
 Deputy National Chief Superintendent: Deputy National Director or Inspector General of the PSP,
Deputy National Chief Superintendent: Deputy National Director or Inspector General of the PSP, -
 Chief Superintendent: commanding officer of a metropolitan / regional command,
Chief Superintendent: commanding officer of a metropolitan / regional command, -
 Superintendent: commanding officer of a district command or second-in-command of a metropolitan / regional command,
Superintendent: commanding officer of a district command or second-in-command of a metropolitan / regional command, -
 Intendent: division commander in a metropolitan / regional command or second-in-command of a district command,
Intendent: division commander in a metropolitan / regional command or second-in-command of a district command, -
 Sub-Intendent: division commander in a district command or second-in-command of a division commanded by an intendent,
Sub-Intendent: division commander in a district command or second-in-command of a division commanded by an intendent, -
 Commissioner: second-in-command of a division commanded by a sub-intendent,
Commissioner: second-in-command of a division commanded by a sub-intendent, -
 Sub-Commissioner: commanding officer of a police squad / police station;
Sub-Commissioner: commanding officer of a police squad / police station;
-
- Police Chiefs
-
 Principal Chief: auxiliary of an unit commanding officer,
Principal Chief: auxiliary of an unit commanding officer, -
 Chief: supervisor of staff and leader of police teams;
Chief: supervisor of staff and leader of police teams;
-
- Police Agents
-
 Principal Agent: a senior principal agent may perform the same functions as a chief, others perform the same functions as an agent,
Principal Agent: a senior principal agent may perform the same functions as a chief, others perform the same functions as an agent, -
 Agent: functions of police constable;
Agent: functions of police constable;
-
- Police Officer Academy (ISCPSI) Students:
-
 Officer Candidate: student of the 5th year of the Training Course for Police Officers (CFOP),
Officer Candidate: student of the 5th year of the Training Course for Police Officers (CFOP), -
 Cadet: student of the 4th year of the CFOP,
Cadet: student of the 4th year of the CFOP, -
 Cadet: student of the 3rd year of the CFOP,
Cadet: student of the 3rd year of the CFOP, -
 Cadet: student of the 2nd year of the CFOP,
Cadet: student of the 2nd year of the CFOP, -
 Cadet: student of the 1st year of the CFOP.
Cadet: student of the 1st year of the CFOP.
-
Romania
| Corps | Corpul ofiţerilor de poliţie (Police Officers' Corps) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Quaestors | Commissioners | Inspectors | |||||||
| Romanian | chestor-general | chestor-șef | chestor-principal | chestor | comisar-șef | comisar | subcomisar | inspector-principal | inspector | subinspector |
| Rank | Quaestor-General | Chief-Quaestor | Principal Quaestor | Quaestor | Chief Commissioner | Commissioner | Subcommissioner | Principal Inspector | Inspector | Subinspector |
| Insignia | ||||||||||
| Corps | Corpul agenţilor de poliţie (Police Agents' Corps) | |||||||||
| Group | Agents | |||||||||
| Romanian | agent-şef principal | agent-şef | agent-şef adjunct | agent principal | agent | |||||
| Rank | Principal Chief Agent | Chief Agent | Deputy Chief Agent | Principal Agent | Agent | |||||
| Insignia | ||||||||||
Russia
The Police of Russia uses the following rank system:
- Cadet (educational institutions of the Ministry of Internal Affairs)
- Private
junior commanding staff
- Junior Sergeant
- Sergeant
- Staff Sergeant
- Sergeant major (Starshina)
- Warrant officer
- Senior warrant officer
Middle commanding staff
- Sub-lieutenant
- Lieutenant
- First Lieutenant
- Captain
Senior commanding staff
- Major
- Lieutenant colonel
- Colonel
General officers
- Police Major General
- Lieutenant-General of Police
- Colonel-General of Police
- General of the Police of the Russian Federation
The rank of Yefeytor is only used by the Internal Troops of the MVD, now the National Guard of Russia.
Serbia
- General of the Police (General policije)
- Chef Police Adviser/Counselor (Glavni policijski savetnik)
- Police Adviser/Counselor (Policijski savetnik)
- Chief Police Inspector (Glavni policijski inspektor)
- Independent police inspector (Samostalni policijski inspektor)
- Police Inspector (Policijski inspektor)
- Police Sergeant (Policijski narednik)
- Junior Police Sergeant 1st Class (Mladji policijski narednik 1 klase)
- Junior Police Sergeant (Mladji policijski narednik)
- Independent Policeman (Samostalni policajac)
- Senior Policeman (Viši policajac)
- Policeman 1st Class (Policajac 1 klase)
- Policeman (Policajac)
- Junior Policeman 1st Class (Mladji policajac 1 klase)
- Junior Policeman (Mladji policajac)
Singapore
Below shown are the rank structure of the Singapore Police Force
- Senior police officers
- Commissioner of Police [CP][14]
- Deputy Commissioner of Police [DCP]
- Senior Assistant Commissioner [SAC]
- Assistant Commissioner [AC]
- Deputy Assistant Commissioner [DAC]
- Superintendent of Police [SUPT]
- Deputy Superintendent of Police [DSP]
- Assistant Superintendent of Police [ASP]
- Inspector of Police [INSP]
- Police officers
- Senior Station Inspector (2) of Police [SSI2]
- Senior Station Inspector of Police [SSI]
- Station Inspector of Police [SI]
- Senior Staff Sergeant [SSSGT]
- Staff Sergeant [SSGT]
- Sergeant [SGT]
- Corporal [CPL]
- Lance Corporal [LC]: Obsolete for the regular force. Currently only available for the Gurkha Contingent.
- Special constable [SC]: Full-time National Servicemen. Promoted FTNS officers will have the SC prefix to their rank, e.g. SC/Cpl, SC/Sgt.
- Police Constable [PC]: This rank is no longer granted to regulars. However, officers below the rank of inspector being discharged from the police force on disciplinary grounds are first reduced to the rank of constable before their discharge.
Sri Lanka
- Gazetted Officers
- Inspector General of Police (IGP)
- Senior Deputy Inspector General of police (SDIG)
- Deputy Inspector General of police (DIG)
- Senior Superintendent of police (SSP)
- Superintendent of police (SP)
- Assistant Superintendent of police (ASP)
- Chief Inspector of police (CIP)
- Inspector of police (IP)
- Sub Inspector of police (SI)
- Non-Gazetted Officers
- Police Sergeant Major (PSM)
- Police Sergeant Class 1 (PS)
- Police Sergeant Class 2 (PS)
- Police Constable Class 1 (PC)
- Police Constable Class 2 (PC)
- Police Constable Class 3 (PC)
- Police Constable Class 4 (PC)
South Africa
As of 1 June 2016, the functional rank structure in the South African Police Service (SAPS) is as follows:[15][16]
- Senior Management - Commissioned officers
- General (Gen) - designation of National Commissioner
- Lieutenant General (Lt Gen) - Actg. National Commissioner, Deputy National Commissioner, Regional Commissioner, Provincial Commissioner, Divisional Commissioner
- Major General (Maj Gen)
- Brigadier
- Commissioned Officers
- Colonel (Col)
- Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col)
- Captain
- Non-commissioned officers
- Warrant Officer (W/O)
- Sergeant (Sgt)
- Constable (Const)
From 1 April 2010 until 1 June 2016, the rank structure was as follows:
- Senior Management - Commissioned officers
- General (Gen) - designation of National Commissioner
- Lieutenant General (Lt Gen) - Actg. National Commissioner, Deputy National Commissioner, Provincial Commissioner, Divisional Commissioner
- Major General (Maj Gen)
- Brigadier
- Commissioned Officers
- Colonel (Col)
- Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col)
- Major
- Captain
- Lieutenant
- Non-commissioned officers
- Warrant Officer (W/O)
- Sergeant (Sgt)
- Constable (Const)
Prior to April 2010, the rank structure was as follows:
- National Commissioner
- Deputy National Commissioner
- Divisional Commissioner or Provincial Commissioner
- Assistant Commissioner
- Director
- Senior Superintendent
- Superintendent
- Captain
- Inspector
- Sergeant
- Constable
- Student
Spain
- Director General of Police (Spanish: Director General de Policia)
- Deputy Director General (Director Adjunto Operativo)
- Sub-Director General (Subdirector General)
- Commissioner General/Division Chief (Comisario General/Jefe de Division)
- Senior Chief (Jefe Superior)
- Principal Commissioner (Comisario Principal)
- Commissioner (Comisario)
- Chief Inspector (Inspector Jefe)
- Inspector
- Sub-Inspector (Subinspector)
- First Class Police Officer (Oficial de Policia)
- Police Officer (Policia)
- Lieutenant General (Teniente General)
- Divisional General (General de División)
- Brigade General (General de Brigada)
- Colonel (Coronel)
- Lieutenant Colonel (Teniente Coronel)
- Major (Comandante)
- Captain (Capitán)
- Lieutenant (Teniente)
- Second Lieutenant (Alférez)
- Chief Warrant Officer (Suboficial Mayor)
- Warrant Officer (Subteniente)
- Sergeant first class (Brigada)
- Staff Sergeant (Sargento Primero)
- Sergeant (Sargento)
- Master Corporal (Cabo Mayor)
- Corporal (Cabo Primero)
- Lance Corporal (Cabo)
- Constable first class (Guardia Civil de 1ª)
- Constable (Guardia Civil)
Basque Country
Ertzaintza - Basque Police
- Superintendent (Basque: Superintendentea)
- Intendent (Intendentea)
- Chief Inspector (Inspektorea)
- Inspector (Inspektoreordea)
- Officer (Ofiziala)
- Non-commissioned Officer (Ofizialordea)
- Constable 1st Class (1. Ertzaina)
- Constable (Ertzaina)
Catalonia
Mossos d'Esquadra - Catalonian Police
- Chief Superintendent (Catalan: Major)
- Superintendent (Comissari)
- Chief Inspector (Intendent)
- Inspector (Inspector)
- Lieutenant (Sotsinspector)
- Sergeant (Sergent)
- Corporal (Caporal)
- Constable (Mosso)
| Rank | Mosso | Caporal | Sergent | Sotsinspector | Inspector | Intendent | Comissari | Major |
| Insignia |  |
Navarre
Policía Foral (Foruzaingoa in Basque) - Navarrese Police
- Foral Police Chief (Spanish: Jefe Policía Foral, Basque: Foruzaingo Nagusia)
- Chief Superintendent (Comisario Principal, Komisario Nagusia)
- Superintendent (Comisario, Komisarioa)
- Inspector (Inspector, Inspektorea)
- Deputy Inspector (Subinspector, Inspektoreordea)^
- Corporal (Cabo, Kaporala)
- Foral Constable (Agente Foral, Foruzaina)
Sweden
| Rank | National Police Commissioner | Police Director | Deputy Police Director | Police Commissioner | Deputy Police Commissioner |
Chief Superintendent | Assistant Police Commissioner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Note | Regional Police Chief, Head of Department |
Deputy Chief of Region, Deputy Head of Dept. |
District Police Chief, Head of Division |
Special assignment | Special assignment | ||
| Swedish Name | Rikspolischef | Polisdirektör (Regionpolischef, Avdelningschef) |
Biträdande Polisdirektör |
Polismästare (Polisområdeschef, Enhetschef) |
Polisöverintendent | Polisintendent | Polissekreterare |
| Insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Rank | Superintendent, Detective Superintendent |
Chief Inspector, Detective Chief Inspector |
Inspector, Detective Inspector |
Sergeant, Detective Sergeant |
Senior Police Constable | Police Constable | Police Trainee |
| Note | Local Police Chief, Head of Section |
Head of Group | After 4 years of employment | ||||
| Swedish Name | Poliskommisarie, kriminalkommissarie (Lokalpolisområdeschef, Sektionschef) |
Poliskommisarie, kriminalkommissarie |
Polisinspektör, kriminalinspektör (Gruppchef) |
Polisinspektör, kriminalinspektör |
Polisassistent | Polisassistent | Polisaspirant |
| Insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Taiwan
- Police Supervisor General (警監特級)
- Police Supervisor Rank One (警監一級)
- Police Supervisor Rank Two (警監二級)
- Police Supervisor Rank Three (警監三級)
- Police Supervisor Rank Four (警監四級)
- Police Officer Rank One (警正一級)
- Police Officer Rank Two (警正二級)
- Police Officer Rank Three (警正三級)
- Police Officer Rank Four (警正四級)
- Police Rank One (警佐一級)
- Police Rank Two (警佐二級)
- Police Rank Three (警佐三級)
- Police Rank Four (警佐四級)
Thailand
สำนักงานตำรวจแห่งชาติ (samnak ngan tamruat haeng chat) - Royal Thai Police
Commissioned officers
- พลตำรวจเอก - Police General (phon tamruat ek)
- พลตำรวจโท - Police Lieutenant General (phon tamruat tho)
- พลตำรวจตรี- Police Major General (phon tamruat tri)
- พลตำรวจจัตวา - Police Brigadier General (not in use now) (phon tamruat jattawa)
- พันตำรวจเอก (พิเศษ) - Police Senior Colonel (equivalent to Police Brigadier General) (phan tamruat ek phiset)
- พันตำรวจเอก - Police Colonel (phan tamruat ek)
- พันตำรวจโท - Police Lieutenant Colonel (phan tamruat tho)
- พันตำรวจตรี - Police Major (phan tamruat tri)
- ร้อยตำรวจเอก - Police Captain (roi tamruat ek)
- ร้อยตำรวจโท - Police Lieutenant (roi tamruat tho)
- ร้อยตำรวจตรี - Police Sub-Lieutenant (roi tamruat tri)
Non-commissioned officers
- ดาบตำรวจ - Police Senior Sergeant Major (dap tamruat)
- จ่าสิบตำรวจ - Police Sergeant Major (ja sip tamruat)
- สิบตำรวจเอก - Police Sergeant (sip tamruat ek)
- สิบตำรวจโท - Police Corporal (sip tamruat tho)
- สิบตำรวจตรี - Police Lance Corporal (sip tamruat tri)
- พลตำรวจ - Policeman/Constable (phon tamruat)
Turkey
Emniyet Genel Müdürlüğü - Turkish Police
- Director General (Emniyet Genel Muduru)
- Director 1st Grade Police Chief for Provinces or departments (1. Sinif Emniyet Muduru)
- Director 2nd Grade Assistant or Vice Police Chief for Provinces or chief sub-departments, or Police Academy Principle (2. Sinif Emniyet Muduru)
- Director 3rd Grade Police Chief for townships or Branches; such as maritime police branch (3. Sinif Emniyet Muduru)
- Director 4th Grade Assistant or Vice Police Chief Police Chief township or chief regional districts or division (4. Sinif Emniyet Muduru)
- Superintendent is a head of service bureaus such as criminal bureau (Emniyet Amiri)
- Chief Inspector Chief Inspector is the supervisor for gruop or head of local police station (Baskomiser)
- Inspector Inspector is the supervisor for squad or assistant head of local police station (Komiser)
- Sub-InspectorSub-Inspector is the assistant supervisor for task team or shift leader for static locations or head of local police station (Komiser Yardimcisi)
- Kıdemli BaşPolis Memuru senior lead-hand police officer
- BaşPolis Memuru lead-hand junior police officer
- Police Officer (Turkish: Polis Memuru)
Ukraine
The National Police of Ukraine uses the following rank system starting 2015:
| Junior officers | Senior officers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder insignia for every day uniform |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rank | Constable, Police officer |
Corporal | Sergeant | Staff sergeant | Junior lieutenant |
Lieutenant | Senior lieutenant |
Captain |
| Supervisory officers | Staff officers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder insignia for every day uniform |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Rank | Major | Lieutenant colonel |
Colonel | Third division general (Major General) |
Second division general (Lieutenant General) |
First division general (Colonel General) |
United Kingdom
While some smaller or area specific police forces (ports, docks, tunnels etc.) may use variations on, or fewer of, these ranks, most territorial police forces and special police forces have a standard set of operational ranks:
The standard Chief Officer ranks outside London are:
Within London's Metropolitan Police Service the Chief Officer ranks are:
- Commander
- Deputy Assistant Commissioner
- Assistant Commissioner of Police of the Metropolis
- Deputy Commissioner of Police of the Metropolis
- Commissioner of Police of the Metropolis
The City of London Police use similar Chief Officer ranks to the Metropolitan Police Service but with fewer ranks:
A police officer with investigative duties, up to and including the rank of Chief Superintendent, is a detective and the word Detective is prefixed to their rank (e.g. Detective Chief Inspector), except for the rank of Police Constable where the word Police is replaced, making them a Detective Constable.
United States
The United States law enforcement ranking model is generally quasi-military in structure. Each level of law enforcement: federal, state, and local have different ranks and varied considerably from agency to agency. There is no nationally set law enforcement rank structure, but they tend to follow similar patterns.
Federal
The Department of Justice, and The Department of Homeland Security (DHS), all contain multiple law Enforcement agencies and are the largest federal departments responsible for law enforcement, however other governmental departments, and agencies have law enforcement bodies. Each federal law enforcement agencies has a unique rank structure. Many federal law enforcement agencies rank structures resemble Military rank structure but have different cogitations regarding responsibilities and duties. In general all law enforcement groups in United States follow a similar pattern shown below.
- Director or Chief (Comparatively General)
- Assistant/ Deputy Director/ Chief (Comparatively Colonel)
- Special Agent in Charge (Comparatively Major)
- Assistant Special Agent in Charge (Comparatively Captain)
- Supervisor Special Agent (Comparatively Lieutenant)
- Special Agent (Comparatively Sergeant)
- Agent (Comparatively Corporal)
- Probationary Agent (Comparatively Private or Cadet)
State
- Chief of State Police (some States use Superintendent, Director or Commissioner)(Often Selected by Governor of State)
- Deputy/Assistant Chief, Superintendent, Director or Commissioner
- Colonel (large States)
- Major
- Captain, or Commander
- Lieutenant
- Staff Sergeant, Sergeant First Class, First Sergeant, Master Sergeant, or Sergeant Major (Large States)
- Sergeant
- Corporal or Senior/Master Trooper/Patrolman
- Trooper, or Patrolman
- Cadet, Recruit, Trainee, or Probationary Trooper/Patrolman
Note: Ranks can be skipped or omitted and structure is often determined by individual States. Structure is usually Pseudo-Military.
County
- Sheriff , Chief, or Chief Sheriff (elected position)
- Under-Sheriff, Deputy Chief (sometimes an elected position)
- Assistant Sheriff (large departments)
- Superintendent or Colonel (large departments)
- Area Commander or Lieutenant Colonel (large departments)
- Major (large departments)
- Captain, or Commander
- Lieutenant
- Staff Sergeant (large departments)
- Sergeant
- Corporal, Senior Deputy, or Senior Deputy Sheriff
- Deputy, or Deputy Sheriff
- Cadet, Recruit, Trainee, or Probationary Deputy
- Note: Ranks can be skipped or omitted and structure is often determined by individual Counties. Structure is usually pseudo-military.
Municipal
- Chief of Police (sometimes an elected position) (some departments use Superintendent, Director or Commissioner)
- Deputy/Assistant Chief or Deputy/Assistant Commissioner (large departments)
- Colonel (large departments)
- Commander (large departments)
- Major (large departments)
- Captain, or Commander
- Lieutenant
- Inspector (large departments)
- Sergeant
- Corporal (sometimes used)
- Police Officer, Detective or Technician
- Cadet, Recruit, Trainee, or Probationary Officer
Note: Ranks can be skipped or omitted and structure is often determined by individual municipalities. Structure is usually pseudo-military.
Venezuela
- Comisonado General
- Comisonado Jefe
- Comisonado Agregado
- Comisonado
- Subcomisionado
- Supervisor Jefe
- Supervisor
- Inspector Jefe
- Inspector
- Subinspector
- Sargento Mayor Supervisor
- Sargento Mayor
- Sargento I
- Sargento II
- Cabo I
- Cabo II
- Distinguido
- Agente[18]
Vietnam
Công an Nhân dân Việt Nam - Vietnam People's Public Security
Commissioned officers
Highest Rank
- Đại tướng Công an - Police General - only held by the Minister of Public Security
- Thượng tướng Công an - Police Colonel General - usually held by the Deputy Ministers of Public Security
- Trung tướng Công an - Police Lieutenant General - usually held by the Directors of General Departments of Ministry, Directors of Hanoi Police Department and Directors of Ho Chi Minh City Police Department
- Thiếu tướng Công an - Police Major General - usually held by Vice Directors of General Departments of Ministry, Directors of Departments of Ministry
Middle Rank
- Đại tá Công an - Police Brigadier - usually held by Directors of Municipality and Province Police Departments
- Thượng tá Công an - Police Colonel - usually held by Chiefs of City, Town and District Police
- Trung tá Công an - Police Lieutenant Colonel - usually held by Chiefs of Ward and Commune Police
- Thiếu tá Công an - Police Major
Low Rank
- Đại úy Công an - Police Captain
- Thượng úy Công an - Police Senior Lieutenant
- Trung úy Công an - Police 1st Lieutenant
- Thiếu úy Công an - Police Sub-Lieutenant ( 2nd Lieutenant).
Non-commissioned officers
- Thượng sĩ - Staff Sergeant
- Trung sĩ - Sergeant
- Hạ sĩ - Corporal
Policemen
- Chiến sĩ bậc 1 - Policeman 1st Class
- Chiến sĩ bậc 2 - Policeman
See also
References
- ↑ http://www.paraentenderdireito.org/livro.html
- ↑ http://www.rcmp-grc.gc.ca/about-ausujet/organi-eng.htm
- ↑ http://www.torontopolice.on.ca/rank/
- ↑ http://vancouver.ca/police/recruiting/police-officers/policing.html#Advancement
- ↑ http://www.edmontonpolice.ca//~/media/EPS%20External/Files/Reports/2008AnnualReport.ashx
- ↑ http://www.chr.alberta.ca/Practitioners/?file=staff/mrs/s/sheriff-security-transport&cf=4#level1
- ↑ http://www.sq.gouv.qc.ca/mission-et-services/publications/csp-information-guide-for-members.pdf
- ↑ http://www.spvm.qc.ca/en/carrieres/5_1_1_3_grades.asp
- ↑ http://www.globalsecurity.org/intell/world/iraq/ips.htm
- ↑ http://www.globalsecurity.org/intell/world/iraq/images/iraq-police-ranks.jpg
- ↑ "Braçais/Distintivos" [Arms/Badges] (in Portuguese). Public Security Police Force of Macau. Archived from the original on 2011-07-22. Retrieved 2010-06-28.
- ↑ "PNP ranks". Norwegian National Police. Retrieved 2010-03-29.
- ↑ "PNP ranks". Philippine National Police. Retrieved 2009-06-30.
- ↑ abbribation chinese
- ↑ http://www.saps.gov.za
- ↑ "Police rank reform the best in years". IOL. 31 May 2016. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- ↑ "Slutredovisning från Genomförandekommittén för nya Polismyndigheten" (in Swedish). SOU/Genomförandekommittén för nya Polismyndigheten. 2015-03-12. Retrieved 3 August 2015.
- ↑ http://www.consejopolicia.gob.ve