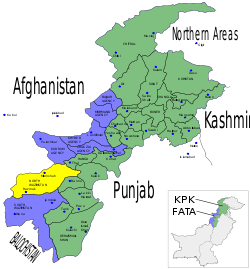
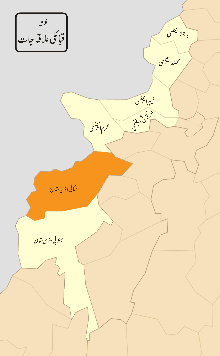
North Waziristan
| North Waziristan اتر وزیرستان | |
|---|---|
| Agency | |
|
| |
| Country | Pakistan |
| Established | 1910 |
| Headquarters | Miranshah |
| Government | |
| • Political agent | Muhammad Yahya Akhunzada |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,707 km2 (1,817 sq mi) |
| Population (1998) | |
| • Total | 361,246 |
| • Density | 77/km2 (200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | PKT (UTC+5) |
| Main language | Pashto |
North Waziristan (Urdu: اتر وزیرستان Uttar Waziristan), abbreviated as NWA, is the northern part of Waziristan, a mountainous region of northwest Pakistan, bordering Afghanistan and covering 11,585 square kilometres (4,473 sq mi). Waziristan comprises the area west and south-west of Peshawar between the Kurram River (Tochi River) to the north and the Gomal River to the south, forming part of Pakistan's Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA). Miranshah is capital of North Waziristan. Bannu, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa lies immediately to the east. The region became an independent tribal territory in 1893, remaining outside of the British empire and Afghanistan. Tribal raiding into British territory was a constant problem for the British, requiring frequent punitive expeditions between 1860 and 1945. The region became part of Pakistan upon its independence in 1947.
Waziristan is divided into two "agencies", North Waziristan and South Waziristan, with estimated populations (as of 1998) of 361,246 and 429,841 respectively. The two parts have quite distinct characteristics, though both tribes are subgroups of the Waziri tribe, after which the region is named,[1] and speak a common Waziri language. They have a famed reputation as formidable warriors and are known for their frequent blood feuds. The tribes are divided into sub-tribes governed by male village elders who meet in a tribal jirga. Socially and religiously, Waziristan is an extremely conservative area. Women are carefully guarded, and every household must be headed by a male figure. Tribal cohesiveness is strong because of "Collective Responsibility Acts" in the Frontier Crimes Regulation.
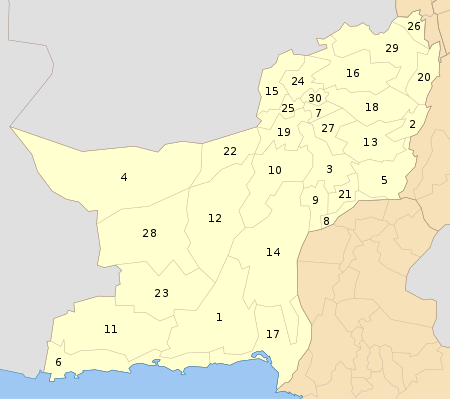
In 1910, North Waziristan Agency was constituted as a full-fledged agency with its headquarters at Miranshah. It is inhabited by the Pashtun Wazir and Dawari tribes. The agency lies from 32.35 degrees to 33.22 degrees north latitude and 69.22 degrees to 70.38 degrees east longitude. It is bounded on the north by Afghanistan, Kurram Agency and Hangu District, on the east by tribal areas adjoining the Bannu and Karak Districts, on the south by South Waziristan Agency and on the west also by Afghanistan. The total area of the agency is 4,707 square kilometres (1,817 sq mi).
Geography
Geographically, the whole of Waziristan is a single unit. However, for administrative convenience it has been split into two agencies – North and South Waziristan. The area has been described as a land of high and difficult hills with deep and rugged defiles. The mountains of North Waziristan are geographically separate from the larger mountain systems of Koh-e-Sufaid in the north and Sulaiman in the south. The Waziristan hills were subject to igneous activity during the late Cretaceous period. The highly mineralised zone of Razmak is connected with it. The mountains and hills form a rampart between Pakistan and Afghanistan. The average height of the Waziristan hills is 1,500–2,500 metres (4,900–8,200 ft) above sea level. The important ranges in the Waziristan hills are Derwesta, Laran, Vezda, Ingame, Shoidar(highest peak Shuiar Sar of NWA is part of this range; visible from Cadet College Razmak also), Shawal, Eblunkai, Alexandra, Muzdak and Zakha.
The Tochi River flowing through the agency has formed the Tochi Pass, through which armies, people and cultures have moved in and out of this region. The Tochi Pass connects Ghazni, Afghanistan with Bannu, Pakistan. The Tochi River has carved a large and important valley which is bounded by hills and mountains on all sides except the eastern side. It is about 100 kilometres (60 mi) in length and opens up into the Indus Valley near Bannu. The Tochi valley is fertile and cultivable. Ketu and Kurram are the two minor rivers which flow in the northern part of the agency.
There are five notable rivers: Tochi, Kaitu, Kurram, Khaisor, and Shaktue. Some notable streams are Khoni Aigad, Chashma Aigad, Saidgi Algad, Kanungo Aigad, Sagga Aigad, Tauda China Algad, Damoma Algad, Tarkhobi Algad, Suedar Aigad.
Mining
The following minerals have been found in the area:
- Copper associated with volcanics at Boya[2] and Manzarkhel Spinkamar (east of Shora-Algad)
- Manganese associated with cherts
- Chromite associated with serpentinites – There are only two mining sites of chromite: at Syed Abad (Mohammad Khel); and Saidgi.
- Gold and diamond mines in Muhammad Khel
- In some hills, ordinary stones are mined for construction of buildings, etc.
Nowadays chromite and copper mining have occurred at Razmak Malakan village.
Climate
The climate of the area is cold in winter and warm in summer. Summer season starts from May and continues until September. June is generally the warmest month. The mean maximum and minimum temperatures during the month of June are 31 and 18 degrees Celsius, respectively. Winter starts in October and continues until April. December, January, and February are the cold months. The mean maximum and minimum temperatures during the month of January are 10 and −2 degrees Celsius, respectively. Rainfall is low except in the Razmak area where the rainfall is slightly higher.
History
During Mughal rule, Waziristan was a part of the Mughal Empire. Once Bahadur Shah, son of Aurangzeb personally visited and received the tribute from the Wazirs and Daurs. After the fall of Mughal Empire, the emerging Sikh Empire and their Khalsa Army could extend their sway to Waziristan. Their short rule of 40 years in this area was confined to sporadic forages. Hari Singh Nalwa ruled this area. The Wazirs and Daurs accepted the influence of the Mughal and Durrani kings, who counted on them as a solid army, ready to help them in emergencies.
Archeological Finds
In 1966 Ahmad Hasan Dani located Buddhist sites from the area:
Coins of the Parthian and Kusana rulers have been found previously in the Shertala plain. Some archeological finds were reported by Sir Aurel Stein. In fact we also located during our visit a Buddhist Stupa site not far from Spinwam. But nothing definite is known about the early history of this region.
The Tochi Valley inscriptions for the first time attest to the presence of the Shahi rulers here ...[3]
British era
When the British took over the administration of the settled district of Bannu in 1849, the tribes of North Waziristan were under the sovereignty of the Kabul government. The British, therefore, entered North Waziristan in 1894 and made agreements with the tribes. The British introduced a regular system of land record and revenue administration for the most fertile part of the Tochi valley. It was later in the year 1910 when North Waziristan was made a full-fledged agency.
In 1935–36, a Hindu-Muslim clash occurred over a Hindu girl of Bannu, who had married a Muslim. The tribesmen rallied around Mirzali Khan, a Tori Khel Wazir, who was later given the title of "the Faqir of Ipi". Jihad was declared against the British. The Faqir of Ipi, with his huge lashkar (force), remained at war until the British retreated in 1947. In spite of his opposition to the newly formed independent Islamic Republic of Pakistan, the jirgas in Waziristan decided in favour of joining Pakistan. The Faqir of Ipi died in 1960.
Ethnic groups and tribes
The chief tribes in North Waziristan are the Utmanzai, Wazirs and Dawars. There are small tribes, like the Gurbaz, Kharsins, Saidgis and Malakshis Mahsuds, and Bangashs. These tribes, except the Saidgis, are Pakhtuns. According to the tribal annals, they are descendants of Karlan, who are descended from Qais Abdur Rashid. Some historians believe that they are ethnically Semites. The traditions of the tribesmen, however, indicate that they are descendants of Karlan and are, therefore, generally accepted as being a tribe of Karlanri Pakhtuns. The Saidgis are the descendants of a Syed who accompanied the founder of the Wazir tribe.
The Wazirs dominate the hilly tracts: Khaisora, Sherathala Plain, Spinwam Mirali, Shewa, Kaitu Valley, Razmak, lower stretches of the Kurram River, upper parts of Tochi Valley beyond Kharakamar and alongside the Tochi Valley such as Anghar kalay, Spalga, Mir khon khel. They are divided into three main sections: Ibrahim Khel, Wali Khel, and Mohmit Khel. These sections are further divided into several sub-sections.
The Dawars are divided into two main sections: Tur Gund and Spin Gund. The inhabitants of village Tappi, village Miranshah, and Issuri Haidar Khel are Tur Gund and the remaining are Spin Gund. In the time of Ahmad Shah Abdali, the total number of Dawars was 12,000 (3,000 Tur Gund 9,000 Spin Gund), and Waziris were 60,000. The traditional jirga of Spin Gund are still called "lazariza" (the meeting of all the 9,000 Spin Gund). Those living under the administrative control of Miranshah tehsil are known as "Upper Dawars". Those living under the administrative control of Mir Ali tehsil are known as Lower Dawars. They have settled in the fertile Tochi valley, mostly on the left bank of the Tochi River, from Khajuri to Kharkamar. They are more educated as compared to Wazirs because most of the educational institutions are in the Dawar area.
The Kharsins are affiliated with Bora Khel and Madda Khel Wazirs. They live near the Durand Line to the northwest of the agency flanked by Madda Khel Wazirs and Saidgis. Mahsuds are the cousins of Wazirs; both have common ancestor: Wazirs. A section of Mahsuds called Bahlol Zai Malakshai occupy a small portion of Razmak surrounded by Bora Khel and Tori Khel Wazirs. The Saidgis occupy Zoi valley, Shawal. Dawegar and Dande plain near the Durand Line. The Kabulkhel contains Miami, Malakshahis, Pipali'Saifali are located in Shewa tehsil. Kabulkhel has two regions in Waziristan: Shawal and Shawa. They migrate to Shawal in summer.
Dress and ornaments
The common dress of tribesmen consists of shirt, trousers, waist-coat, sheet of cloth, turban, and Chappal. A Wazir woman wears a sleeved blouse or petticoat and a long heavy shirt with trousers. She covers her head and body with a sheet of cloth. A married woman wears coloured trousers while an unmarried woman wears simple trousers. For festivals and marriages, Wazir women put on colourful and ornamented blouses and multi-coloured frocks sometimes made of 40 metres (130 ft) cloths. To further adorn themselves, the women put on rectangular pieces of silver and gold that hang on their forehead and side-ways down to ear. While the dress of Dawar people is somewhat the same as the Wazirs, there are some differences due to regional, and climate variations. Dawar wear almost all kind of dresses usually used throughout Pakistan.
Food
The staple food of the tribesman is wheat or maize bread. Milk is consumed in its various forms. Roasted meat larmin is relished. The people of Waziristan generally like a fried goat dish called palawoo, served in hilly areas.
Dwelling
The Dawars live in houses close together in a compact area. Large joint Waziri families live either in one house called ket or kot or in houses adjacent to one another, but separated from the houses of the other families. A walled enclosure of mud or mud and stones three to five metres (16.4 ft) high is called a kot. Most kots have a fort-like structure, with a tower in the centre, which is used as a strategic point for fighting with the enemy when hostilities break out. Every section in a village has a Masjid and a common sitting place. One or more households have a private guest house hujra attached to the house. In a house, there may be one or several rooms. Wazirs people mostly live near mountainous areas and they have a generally different lifestyle from the Dawar tribes, who live near rivers and on plains.
Occupation
Due to the rugged nature of the terrain and their lack of education, many inhabitants believe they must depend upon government services. Many emigrate abroad to earn livelihoods . Local people have also invested in transportation-related businesses. Waziri tribes generally run businesses, while Dawars tribes are more heavily employed through government services. Emigres from Waziristan tend to prefer medical education, when available to them.
Places of interest
Miranshah is the headquarters of North Waziristan Agency, It is connected with Bannu and other important places in the agency by metalled roads. This town houses the offices of all government departments in the agency and also serves as a market centre for people of the area.
Razmak valley is a summer resort.[4]
Administrative setup
The agency is under the general charge of a Political Agent who administers civil, criminal and revenue cases in accordance with Frontier Crimes Regulation and Customary Law. The North Waziristan Agency consists of three sub-divisions and nine Tehsils. The Miranshah sub-division comprises the Miranshah, Ghulam Khan, and Datta Khel tehsils. The Mir Ali sub-division contains the Mir Ali, Spinwam, and Shewa tehsils. The Razmak sub-division consists of the Razmak, Dossali, and Garyum tehsils. Each of the sub-division is headed by an Assistant Political Officer/Assistant Political Agent. The Political Agent is assisted by three Assistant Political Agents in criminal cases and other official work including matters maintaining law and order in the agency. Assistant Political Agents assist the Political Agent in tackling problems of the agency. They perform their duties like a Liaison Officer between the Political Agent and the tribes. They also decide cases of minor criminal nature and civil suits.
A new post of Additional Political Agent has been established who looks after the developmental sector of the whole agency. The need was felt for reason of high level intervention in developmental sector by both governmental and non-governmental organizations. In addition to these duties the Additional Political Agent acts as Political Agent in his absence. Furthermore, all the Line Directorates work under supervision of Additional Political Agent.
Political Tehsildars and Political Naib- Tehsildars are in charge of Tehsils and their main duty is to control the tribes and maintain law and order within their own areas. They are answerable to the Political Agent through the Assistant Political Agent. They deal with all cases occurring in the protected area of their respective Tehsils. Land revenue administration in some parts of the agency is carried on exactly on the same lines as in the settled districts of Pakistan. The Frontier Crimes Regulation is applicable in this area. Cases occurring in the unprotected area are decided by the tribes themselves through their elders who are known as Maliks and Motabars. The Maliki system introduced by British government was the same in North Waziristan Agency as functioning in other FATA. Maliks use to work like a medium between administration and the Qaum or tribe. A Maliki is hereditary and devolves on the son and his son so on and so both for which regular benefits and subsidies are sanctioned from time to time. Lungi system known as Sufaid Resh is slightly lower form of Maliki. In North Waziristan Agency there are 1620 Maliks and Lungi holders.
Pakistan's new Waziristan strategy
On 4 June 2007, the National Security Council of Pakistan met to decide the fate of Waziristan and take up a number of political and administrative decisions to control "Talibanization" of the area. The meeting was chaired by president Pervez Musharraf and it was attended by the Chief Ministers and Governors of all four provinces. They discussed the deteriorating law and order situation and the threat posed to state security.[5]
The government decided to take a number of actions to stop the "Talibanization" and crush the armed militancy in the Tribal regions and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
The NSC of Pakistan has decided the following actions will be taken to achieve the goals:
- Deployment of unmanned reconnaissance planes
- Strengthening law-enforcement agencies with advanced equipment
- Deployment of more troops to the region
- Operations against militants on fast-track basis
- Focused operations against militant commanders
- Action against madrassah's preaching militancy
- Appointment of regional coordinators
- Fresh Recruitments of police officers in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
The ministry of interior has played a large part in the information gathering for the operations against militants and their institutions. The Ministry of Interior has prepared a list of militant commanders operating in the region and they have also prepared a list of seminaries for monitoring.
The government is also trying to strengthen the law enforcement in the area by providing the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Police with weapons, bullet-proof jackets and night-vision devices. The paramilitary Frontier Corps will be provided with artillery and APC's. The state agencies are also working on studying ways to block FM frequencies of illegal FM radio channels.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Tribe: Ahmadzai Wazir" (PDF). Naval Postgraduate School.
- ↑ Nawazkahn, M. "PAKISTAN MINERAL DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION-FATA-DC PESHAWAR". GEOLOGICAL REPORT OF SHINKAI COPPER MINERALIZATION NORTH WAZIRISTAN AGENCY. Retrieved 19 October 2010.
- ↑ Leelananda Prematilleka; Kārttikēcu Intirapālā (1978). Senarat Paranavitana, Prematilleka, Johanna Engelberta Lohuizen-De Leeuw, eds. Senarat Paranavitana commemoration volume. Leiden: Brill. p. 48. ISBN 9789004054554.
- ↑ Yusufzai, Rahimullah. "24 FC soldiers die in N Waziristan suicide bombing". The Indonesian Embassy, Islamabad Pakistan. Retrieved 19 October 2010.
- ↑ Perlez, Jane (30 June 2007). "Taliban Spreading, Pakistani President Is Warned". The New York Times. Retrieved 19 October 2010.
- ↑ Khan, Ismail (2007). "Plan ready to curb militancy in Fata, settled areas". Dawn. Newsweek international edition. Pakistan. Archived from the original on 11 July 2007. Retrieved 2007-06-27.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Waziristan. |
- Waziristan and Mughal empire
- Nehru in Waziristan
- Sketch map of Waziristan
- Mehsuds and Wazirs, the King-makers in a game of thrones
- Lawrence of Arabia in Waziristan