North Kent Line
| North Kent Line | |
|---|---|
|
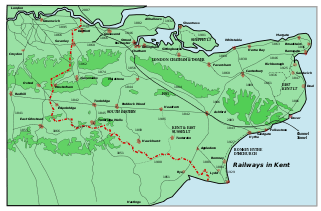
The North Kent Line, shown with other railway lines in Kent. | |
| Overview | |
| Type | Commuter rail, Suburban rail |
| System | National Rail |
| Status | Operational |
| Locale |
Greater London South East England |
| Termini |
London Charing Cross London Cannon Street Gillingham Dartford |
| Operation | |
| Owner | Network Rail |
| Operator(s) | Southeastern |
| Depot(s) |
Slade Green Grove Park Gillingham |
| Rolling stock |
Class 375 "Electrostar" Class 376 "Electrostar" Class 395 "Javelin" Class 465 "Networker" Class 466 "Networker" |
| Technical | |
| Number of tracks | 2 |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge |
| Electrification | 750 DC third rail |
The North Kent Line is a railway line which runs from Lewisham Vale junction[1][2] (at the country end of St Johns station), where it splits from the Southeastern Main Line, to Rochester Bridge junction[3][4] (just south of Strood station), then links up with the Chatham Main Line.
History
Construction
The North Kent Line was the means by which the South Eastern Railway (SER) was able to connect its system to London at London Bridge. In 1846 the SER purchased the Thames and Medway Canal tunnel near Higham and laid railway tracks through it; in 1847 trains were working through from the Strood terminus, on the River Medway to Gravesend. From 30 July 1849 the line was extended, via Blackheath, to a junction with the London and Greenwich Railway at North Kent East Junction, near Deptford, and through trains were now working.
Electrification
The line is electrified (750 V DC third rail). Electrification was initially to Dartford (6 June 1926) and was extended to Gillingham by World War Two.
The Route and Services
The North Kent Line is a high-frequency line, with all stations in the London area being served by at least 4 trains per hour, with Lewisham 14tph.
London Charing Cross to Gillingham 2tph fast, calling at Waterloo East, London Bridge fast to Lewisham (for Docklands Light Railway), Blackheath, Charlton, Woolwich Arsenal (for the Docklands Light Railway), Abbey Wood (Future interchange with Crossrail) fast to Dartford, then Greenhithe (for Bluewater), Gravesend then all stations to Gillingham.
London Cannon Street to Slade Green all stations via Greenwich 6tph, of which 2tph continue to Dartford, 2tph continue back to Cannon Street via Bexleyheath and Lewisham on the Bexleyheath line and 2tph to Cannon Street via Sidcup and Hither Green on the Dartford Loop Line.
London Cannon Street to Plumstead 2tph, Semi Fast calling at London Bridge, New Cross, Lewisham, Blackheath, Charlton, Woolwich Arsenal and Plumstead, this service does not call at St. Johns and Woolwich Dockyard.
Former services
From 1999–2002 there were semi-fast trains starting from Plumstead to London Victoria briefly resuming a 1980s service pattern. This service was for the Millennium Dome, the service called at, Woolwich Arsenal, Charlton, Blackheath, Lewisham, Peckham Rye then non-stop to London Victoria, there was also an early morning semi fast service to London Blackfriars from Dartford in the 1980s.
There were plans in 2003 to have a Plumstead to Clapham Junction cross south London service but it never came into fruition
Future
Abbey Wood is to become the eastern terminal for Crossrail. A possible extension of Crossrail to Gravesend has been safeguarded.
Stations
Train services working the Line today take the following route; the first ten miles (16 km) passes through many tunnels, included on the list:
- Lewisham
- Blackheath – here is the junction for the Bexleyheath Line
- Blackheath Tunnel [1 mile (1.6 km) in length]
- here is the freight branch to Angerstein Wharf
- junction for the line from Greenwich and the eastern connection with the London and Greenwich Railway, opened in 1878
- Charlton
- Charlton Tunnel [154 yd (138 m)]
- Mount Street Tunnel [121 yd (108 m)]
- Dockyard Tunnel [121 yd (108 m)]
- Woolwich Dockyard
- Coleman Street Tunnel [89 yd(80 m)]
- George IV Tunnel [238 yd (214 m]
- Calderwood Street Tunnel [58 yd (52 m)]
- Cross Street Tunnel [134 yd (120 m)]
- Woolwich Arsenal
- Plumstead – here the Royal Arsenal railway system connected with the main line
- Church Manor Way Halt – closed
- Abbey Wood
- Belvedere
- Erith
- Slade Green -includes the large carriage-servicing depot
- here is the triangular junction with the Bexleyheath Line
- here is the triangular junction with the Dartford Loop Line
- Dartford
- Stone Crossing
- Greenhithe – to which has been added "for Bluewater"
- Greenhithe Tunnel [253 yd (228 m)]
- Swanscombe
- Northfleet – this station is only 305m or so from Ebbsfleet International as the crow flies, but it is at least a 1km walk between the two stations.
- Gravesend: was originally named Gravesend Central to differentiate it from the ex-London, Chatham and Dover Railway station at Gravesend West which closed in 1968
- Milton Road Halt-closed
- Denton Halt- closed
- Milton Range Halt-closed
- Hoo Junction Staff Halt, where the line branches ("The Hundred of Hoo Railway") to Grain. Currently for freight services (not electrified)
- Higham
- Higham and Strood tunnel – actually two tunnels [total 3931 yd (3595 m)] with a gap of 100 yards (91 m) between.
- Strood – the junction for the Medway Valley Line.
The North Kent Line connects with the LCDR Chatham Main Line at Rochester Bridge Junction, about 200 m beyond Strood station. It totals some 30 miles (48 km) in length.
Service patterns
As of July 2015, the service pattern is:
Off-peak & Saturday:
- 2tph between London Cannon Street & Dartford via Greenwich (stopping service)
- 2tph between London Cannon Street & Slade Green via Greenwich, continuing to London Cannon Street via the Bexleyheath Line (stopping service)
- 2tph between London Cannon Street & Slade Green via Greenwich, continuing to London Cannon Street via the Dartford Loop Line (stopping service)
- 2tph between London Charing Cross & Gillingham (semi-fast)
- 2tph between London Charing Cross & Gravesend via Dartford Loop Line
- 2tph between St Pancras International & Ramsgate, continuing to St Pancras International via the Kent Coast Line and High Speed One, via High Speed One
Sunday:
- 2tph between London Cannon Street & Dartford via Greenwich (stopping service)
- 2tph between London Bridge & Plumstead via Greenwich (stopping service)
- 2tph between London Charing Cross & Gillingham (semi-fast)
Peak hour frequencies vary, with services from the Bexleyheath and Dartford loop lines also running to and from stations to Gillingham.
References
- ↑ Quail Map 5 – England South [page 3] Sept 2002 (Retrieved 25 December 2011)
- ↑ Network Rail (April 2001). Southern Zone Sectional Appendix. Module SO. p. 1/37 SO130. (Retrieved 25 December 2011)
- ↑ Quail Map 5 – England South [page 7] Sept 2002 (Retrieved 25 December 2011)
- ↑ Network Rail (April 2001). Southern Zone Sectional Appendix. Module SO. p. 1/15 SO130. (Retrieved 25 December 2011)