Naming laws in the People's Republic of China
Naming laws in the People's Republic of China (excluding Hong Kong and Macau, as well as the Republic of China situated on the islands of Taiwan, Penghu, Kinmen and Matsu) are based on technical capability rather than the appropriateness of words (as opposed to naming laws in Japan, which restrict the Kanji which can be used based on appropriate taste, as well as readability by all people). Although it is advised for parents to name their children so that others are able to easily read their names, there are no restrictions on the complexity of Chinese characters used, provided that there are no technical issues in doing so (see below). The use of Simplified characters is advised over Traditional Chinese characters; however, this is not strictly enforced.
Details
"General Principles of Civil Law" Article 99 guarantees citizens the right to a name and the choice of naming therein.[1] The right of self-naming permits the surname, although naturally obtained from the paternal side, to be taken from either parent if desired (such as in the case of a dispute between parents) under Article 22 of the "Marriage Law". Thus, the government does not interfere with the will of the person or their parents in the selection of a surname, provided that it is taken from one parent. Citizens also have the right to select their given names and aliases, in which the government has no right to interfere.
There are also no restrictions on previously used names by the government, which fully permits the usage of "well-known" names. It is not illegal to name a child after a famous celebrity, company, or product, as copyright and trademark laws do not apply to personal names. Consequently, this is able to lead to legal issues regarding intellectual property rights and legal matters, as the person is then known by the name given according to law, which opens the possibility for confusion where a personal name is exactly the same to a company or another person, such as during a court case or the creation of legal documents.[1]
Latin characters, numerals and other non-Chinese symbols are prohibited, as they do not constitute part of a Chinese name under government law. Only Chinese characters are permitted; however, characters which are unable to be input on computers are also disallowed. There are no limits on the number of characters used, as this may vary depending on the name (typical Chinese names on average constitute 2 to 3 characters, with 4 or more characters being rare; however, non-Han ethnic groups such as Mongols, Tibetans and Uighurs have many syllables after transliteration into Standard Chinese).
There are no laws which restrict a person's surname to one character like most Han Chinese names, since some people of Han Chinese ethnicity have Chinese compound surnames, and it is very common for foreign residents and ethnic minorities to have long surname transcriptions. However, since the People's Republic of China government does not recognise Mongolian clan names as surnames, persons of Mongol ethnicity usually only have a registered given name and no surname (which are absent on their identification cards, whilst their passports would have "XXX" in the surname field), although some individuals choose to adopt a single-character Han Chinese surname that resembles an abbreviation of their clan name.
Technical issues
There are over 70,000 known Chinese characters, yet approximately only 32,232 are supported for computer input,[2] including both Traditional and Simplified characters (see GBK etc.). As the government database of personal names is maintained digitally on government networks, input of rarer characters becomes virtually impossible, thus creating an irremovable restriction on permitted names. All citizens within the People's Republic of China must have their details registered on the government computer network, while those over the age of 16 must carry an identification card, known in China as a Resident Identity Card at all times. As these processes are all done electronically, having a name which is not supported by electronic input makes government registration and the management of ID cards much more difficult.
Notable cases
Ma Cheng

Ma Cheng (Chinese: 马𩧢 (some browsers will be unable to display the second character ![]() , which is three 馬 horses placed horizontally), pinyin: Mǎ Chěng) is a woman from Beijing who, due to her obscure name, frequently encounters issues regarding name registration in places such as airports and police stations.[4] Ma explained on BTV-7 [5] that her parents were inspired by a trend where given names are made up of a tripled surname, as in Jin Xin 金鑫, Xiao Mo 小尛, Yu Xian 魚鱻 and Shi Lei 石磊, and so her grandfather found her name in the Zhonghua Zihai, the largest Chinese character dictionary. Pronounced "Cheng", this character can be found in the Kangxi Dictionary, where it is listed as a variant character of 骋 (gallop). There is also the comparatively more common stacked character 骉, which doesn't accurately reflect her name either, as it has a different pronunciation. While some vendors may write her name by hand, those that are strictly electronically managed, such as the Public Security Bureau, are unable to correctly enter her name. Because of this, some computers record her name as 马CHENG or 马马马马. (Compare this practice with the previous technical issues of inputting the Chinese name of the Taiwanese singer David Tao (Chinese: 陶喆; pinyin: Tao Zhe), where before the input of zhe 喆 became supported on computers, many media sources often rendered his name as Tao Jiji 陶吉吉, using two ji 吉 in place of the zhe 喆.)[6]
, which is three 馬 horses placed horizontally), pinyin: Mǎ Chěng) is a woman from Beijing who, due to her obscure name, frequently encounters issues regarding name registration in places such as airports and police stations.[4] Ma explained on BTV-7 [5] that her parents were inspired by a trend where given names are made up of a tripled surname, as in Jin Xin 金鑫, Xiao Mo 小尛, Yu Xian 魚鱻 and Shi Lei 石磊, and so her grandfather found her name in the Zhonghua Zihai, the largest Chinese character dictionary. Pronounced "Cheng", this character can be found in the Kangxi Dictionary, where it is listed as a variant character of 骋 (gallop). There is also the comparatively more common stacked character 骉, which doesn't accurately reflect her name either, as it has a different pronunciation. While some vendors may write her name by hand, those that are strictly electronically managed, such as the Public Security Bureau, are unable to correctly enter her name. Because of this, some computers record her name as 马CHENG or 马马马马. (Compare this practice with the previous technical issues of inputting the Chinese name of the Taiwanese singer David Tao (Chinese: 陶喆; pinyin: Tao Zhe), where before the input of zhe 喆 became supported on computers, many media sources often rendered his name as Tao Jiji 陶吉吉, using two ji 吉 in place of the zhe 喆.)[6]
Zhao C
Zhao C (Chinese: 赵C; pinyin: Zhào C) is a well-known example, having attracted much media attention [7][8] due to a bizarre case regarding a forced name change by the government due to naming regulations. This case is the first of name rights in the People's Republic of China.[9] Zhao, whose personal name is the Latin alphabet letter C, can no longer use his name, as the government does not accept Latin characters in Chinese names.[10] The 22-year-old man, having used the given name "C" for his entire life, was refused the right to continue using his name when he was required to update his ID card to a second-generation version.[11][12] The local Public Security Bureau informed him that his name violated the rules, and that their computers were not equipped to handle non-standard characters.[13] In Pinyin, his name has a pronunciation similar to cí (雌), rather than xī (西).[14] Zhao could not continue using his name despite a court hearing, as he did not provide the lower court with evidence that the Latin character "C" is part of the national standard for "numbers and symbols" of the People's Republic of China.[6][15][16]
Wang "At"
Wang "At" (Chinese: 王@; pinyin: Wáng "at") is the name that a Chinese couple attempted to give to their newborn baby. It was subsequently rejected.[17][18] The couple claimed that the character used in e-mail addresses echoed their love for the child, where in Chinese, "@" is pronounced as "ai-ta", which is similar to 爱他, literally "love him".[19][20] The incident became widely known, and even covered by Reuters.[21]
Other
- Xin Ge (辛哿) – A man with a name meaning "satisfactory" and "fine", who also has difficulty in the registering of his name due to an unsupported character.[22][23]
See also
- Chinese name
- Chinese surname
- Chinese input methods for computers
- Naming law in Sweden - for similar cases in Sweden
References
- 1 2 什么是姓名权? – 法律快车知识. Lawtime.cn (2009-03-01). Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ Lafraniere, Sharon (21 April 2009). "Name Not on Our List? Change It, China Says". The New York Times.
- ↑ Note: The character which appears on the ID card is a Simplified Chinese variant character of
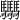 , adapted to match other characters in the PRC, using the simplified 马 (ma, "horse") character. As of April 2009, there is no Simplified Chinese variant of "Cheng" supported by Unicode.
, adapted to match other characters in the PRC, using the simplified 马 (ma, "horse") character. As of April 2009, there is no Simplified Chinese variant of "Cheng" supported by Unicode. - ↑ Living with an obscure name – DANWEI. Danwei.org. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ Video from BTV-7. Leitie.com. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- 1 2 LaFraniere, Sharon (21 April 2009). "Name Not on Our List? Change It, China Says". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 April 2009.
- ↑ 专家称赵C姓名权官司意义重要 促使完善法律法规
- ↑ 一审胜诉 赵C还叫赵C
- ↑ 赵C姓名权庭审花絮:“左半月形”成法庭流行语 – Sina.com.cn. News.sina.com.cn. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ Chinese student, police don't "C" eye-to-eye over name on ID card – XINHUA. News.xinhuanet.com (2009-02-26). Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ 中国姓名权第一案终审达成和解 赵C要改名字(图)
- ↑ http://jiangxi.jxnews.com.cn/system/2009/02/26/011036313.shtml
- ↑ Zhao "left crescent" needs a new name – DANWEI. Danwei.org. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ 英文字母入姓名不符合我国法律
- ↑ “赵C姓名权”案二审判其改名 案件引发的思考 Archived April 21, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ 双方达成和解 赵C还得改名
- ↑ Problems with crazy characters – DANWEI. Danwei.org. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ 新闻出版总署副署长柳斌杰:新媒体发展的现状与趋势 – 人民网. Media.people.com.cn. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ 汉语公布171新词. News.thebeijingnews.com (2007-08-17). Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ 父亲喜欢新事物 儿子取名叫“@” – XINHUA. News.xinhuanet.com. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ Couple in China tried to name baby '@'. Reuters.com (2007-08-16). Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ 公安系统安装软件应对32个身份证冷僻字(图). Tech.sina.com.cn. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
- ↑ Acceptance comes for obscure characters – DANWEI. Danwei.org. Retrieved on 2012-01-08.
External links
- Mair, Victor (21 April 2009). "A Limitation on Names in the PRC". Language Log. Retrieved 27 June 2009.