McConnell equation
McConnell equation describes the proportional dependence of the hyperfine splitting constant  on the spin density
on the spin density  (the probability of an unpaired electron being on a particular atom) in aromatic radical compounds such as benzene radical anion
(the probability of an unpaired electron being on a particular atom) in aromatic radical compounds such as benzene radical anion 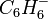 .
.

 is an empirical constant that can range from 2.0 to 2.5 mT.
is an empirical constant that can range from 2.0 to 2.5 mT.
History
The equation is named after Harden M. McConnell of Stanford University, who first presented it in 1956 in an article in the Journal of Chemical Physics.[1]
References
Peter Atkins, Julio de Paula, Atkins' Physical Chemistry, 9th ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford, 14, 556
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 1/9/2013. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.