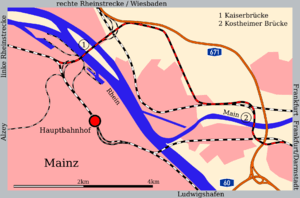
Mainz rail bypass
| Mainz bypass | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Kostheim Bridge over the Main | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Native name | Umgehungsbahn Mainz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Locale | Rhineland Palatinate and Hesse, Germany | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line number | 3525 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line length | 15.1 km (9.4 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrification | 15 kV/16.7 Hz AC overhead catenary | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Mainz bypass railway (German: Umgehungsbahn Mainz) is a bypass around the Mainz Hauptbahnhof node primarily used for freight in the German states of Hesse and Rhineland Palatinate.
History
Even after Mainz Hauptbahnhof was moved to its present location in 1884, it soon became a bottleneck for traffic again. This was mainly due to the need to use the Mainz Tunnel, which only had two tracks.
In 1900, the Prussian-Hessian Railway Company (Königlich Preußische und Großherzoglich Hessischen Staatseisenbahnen or K.P.u.G.H.St.E.), supported by the governments of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Grand Duchy of Hesse, decided to solve this problem by building a rail bypass. While this required a complex route involving bridges, it avoided the need for freight traffic to run through Mainz Hauptbahnhof. The line entered operation on 2 May 1904.
Route
The 15.1 km long line begins in Mainz-Mombach station. It crosses the Rhine on the Emperor Bridge, which was built for the line, reaching an area that is now in the city of Wiesbaden and crosses the Taunus Railway south of Wiesbaden Ost station. There are grade separated entrances and exits towards Wiesbaden and Koblenz.
The line runs in a wide arc around Mainz-Kastel. In Mainz-Kostheim it crosses the Taunus Railway again; at Kostheim junction it is possible to transfer to the line to Frankfurt.
Then it reaches the Kostheim Bridge over the Main, crosses the Rhine-Main Railway and runs in a wide arc into Mainz-Bischofsheim station. From there it is possible to continue via the Main Railway to Frankfurt Hauptbahnhof (and formerly to the now demolished Frankfurt main freight yard) and the Rhine-Main Railway to Darmstadt Hauptbahnhof.
The construction of the bypass allows the operation of trains from Frankfurt and Mainz-Bischofsheim freight yard over the Mainz–Ludwigshafen line towards Worms, without reversal in Mainz Hauptbahnhof. This route, however, is rarely used due the need to run through Mainz Tunnel.
Igelstein connecting curve
A single-track connecting curve from the former Igelstein junction to the East Rhine Railway has been under construction since early 2011 under the “seaport hinterland transport emergency program” (Sofortprogramms Seehafenhinterlandverkehr).[2] According to the tender, this involves a 1,200 m long single-track connection, including two ground frames.[3] The curve allows all freight trains through the district of Mainz-Kastel to run via the bypass, avoiding conflict with regional passenger services.
Monuments
This Mainz bypass runs over a series of bridges. The historic bridges on the bypass were crossings over infrastructure and rivers. These structures on a large scale had a revivalist design, while numerous details were in the Art Nouveau style, such as the bridge railings. Part of this original design has been preserved, while other parts, especially the Kaiser Bridge, were destroyed or damaged during the Second World War and rebuilt after the war in highly simplified forms. Monuments that will be evaluated under the Hessian Heritage Act include:
- the Kaiser bridge over the Rhine and
- the Hochheim Bridge over the Main.
Services
The northern section of the line, north of Kostheim junction, was and is used almost exclusively for freight traffic.
Scheduled passenger trains occasionally run on this section of line, such as the Jan Kiepura, which runs between Amsterdam and Warsaw via Frankfurt, (with a through coach to Moscow). In addition, passenger trains are diverted over the section during unscheduled disruptions on other lines and as a result of construction projects.
South of Kostheim junction the line is used by scheduled trains S-Bahn line S 9 operated by the Rhein-Main-Verkehrsverbund.
Notes
- ↑ Eisenbahnatlas Deutschland (German railway atlas). Schweers + Wall. 2009. ISBN 978-3-89494-139-0.
- ↑ "Reports 16/10945" (PDF) (in German). Deutscher Bundestag. 14 November 2008. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
- ↑ "Tender request for "Neubau Igelsteinkurve"" (in German). Deutsche Bahn. 14 April 2010. Retrieved 25 November 2011.
References
- Landesamt für Denkmalpflege Hessen, ed. (2005). Eisenbahn in Hessen. Kulturdenkmäler in Hessen. Denkmaltopographie Bundesrepublik Deutschland (in German). 2.2. Stuttgart: Theiss Verlag. pp. 888ff. ISBN 3-8062-1917-6.