Lord Derby's parakeet
| Lord Derby's parakeet | |
|---|---|
_-captive-8a.jpg) | |
| A pair - male on left and female on right | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Psittaciformes |
| Superfamily: | Psittacoidea |
| Family: | Psittaculidae |
| Subfamily: | Psittaculinae |
| Tribe: | Psittaculini |
| Genus: | Psittacula |
| Species: | P. derbiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Psittacula derbiana (Fraser, 1852) | |
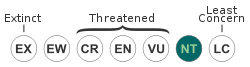
The Lord Derby's parakeet (Psittacula derbiana), also known as Derbyan parakeet, is a monotypic parrot species,[2] which is confined to small pocket of moist evergreen forest in the hills and mountains of the Indian states of Arunachal Pradesh and Assam, and adjoining parts of Tibet, Sichuan and Yunnan in China.[1] The species suffers from cutting of old trees (important for nesting sites) and poaching for the illegal wildlife trade.[1] In 2011, its status was updated from Least Concern to Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List.[1] The adult male and female are easily distinguished because they have different beak colours and slightly different plumage.[1]
The name of this bird commemorates Edward Stanley, 13th Earl of Derby.
Lord Derby's parakeets feed on fruits, berries, seeds, and leaf buds, occasionally foraging in gardens and fields.
Description

Lord Derby's parakeets are 45–50 cm (18–20 in) in length and are sexually dimorphic.[1] They have a mostly green plumage over their dorsal surface (i.e. from behind), black lores and lower cheeks, a bluish-purple crown and pale yellow eyes. The throat, breast, abdomen and under-wing coverts are greyish blue to lavender. The thighs and vent area are yellowish green with blue edging on some of the feathers. The tail feathers are shades of green, some edged with blue. Male birds have a red upper mandible with a yellow tip, while the lower mandible is black. The females have an all-black beak.
Immature Lord Derby's parakeets are duller in colour than the adults. Juvenile birds have green crowns, orange-red upper and lower mandible (beak), and their irises are dark and do not lighten until they reach maturity between two and three years of age.
Sexual dimorphism
- Adult male
 The adult male has a red upper mandible
The adult male has a red upper mandible Male
Male Male pet kept in China
Male pet kept in China
- Adult female
_-female2.jpg) A female pet in Tibet. The adult female has an all black beak.
A female pet in Tibet. The adult female has an all black beak._-Beijing_-captive-8.jpg) A female pet in China
A female pet in China
Reproduction

Breeding season usually begins between April and June. The female lays a clutch of two to four eggs (36.1 mm × 27.7 mm [1.42 in × 1.09 in]) in nest holes of trees. The young hatch after an incubation period of about 23 days and will fledge after 8 to 9 weeks.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 BirdLife International (2012). "Psittacula derbiana". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ "Zoological Nomenclature Resource: Psittaciformes (Version 9.022)". www.zoonomen.net. 31 March 2009.
External links
- World Parrot Trust Parrot Encyclopedia - Species Profiles
- Lord Derby's parakeets in capital of Tibet
- Derbyan pictures and links
- BirdLife Species Factsheet
- Oriental Bird Images: Derbyan parakeet Selected photos
- http://animal-world.com/encyclo/birds/parakeets/DerbyanParakeet.php#
- http://home.wanadoo.nl/psittaculaworld/PsittaculaWorld.htm
- http://www.ruffledfeathersaviary.com/derbyan_photos.htm