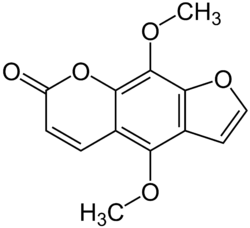
Isopimpinellin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4,9-dimethoxyfuro[3,2-g]chromen-7-one | |
| Other names
5,8-Dimethoxypsoralen 5,8-Dimethoxypsoralene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 482-27-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28853 |
| ChemSpider | 61391 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.166.737 |
| KEGG | C02162 |
| PubChem | 68079 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 246.21 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Isopimpinellin is a natural product synthesized by Umbelliferae (or Apiaceae), also known as the carrot or parsley family. It can be found in celery, garden angelica, parsnip, fruits and in the rind and pulp of limes.[1] There have been several studies looking into the effects of Isopimpinellin and other so-called naturally occurring coumarins (such as bergamottin and Imperatorin) as anticarcinogens.[1][2] These studies have shown possible inhibition of 7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)anthracene, which are initiators of skin tumors.[1] Evidence has also been reported that links these compounds to the inhibition of breast cancers.[2]
Biosynthesis
Isopimpinellin is a furocoumarin thought to be synthesized through the mevalonate pathway via addition of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) to a modified coumarate known as umbelliferone. The biosynthesis is shown below:[3]

References
- 1 2 3 Kleiner, Heather E.; Suryanarayana V.Vulimiri; Matthew F.Starost; Melissa J.Reed; John DiGiovanni (2002). "Oral administration of the citrus coumarin, isopimpinellin, blocks DNA adduct formation and skin tumor initiation by 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene in SENCAR mice". Carcinogenesis. 23 (10): 1667–1675. doi:10.1093/carcin/23.10.1667. PMID 12376476.
- 1 2 Prince, Misty; Cheryl T.Campbell; Taylor A.Robertson; Amy J.Wells; Heather E.Kleiner (2006). "Naturally occurring coumarins inhibit 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene DNA adduct formation in mouse mammary gland". Carcinogenesis. 27 (6): 1204–13. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgi303. PMID 16387742.
- ↑ Dewick, Paul M. (2009). Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach (3rd ed.). UK: John Wiley & Sons Ltd. ISBN 0-471-97478-1.