Henry Grace à Dieu
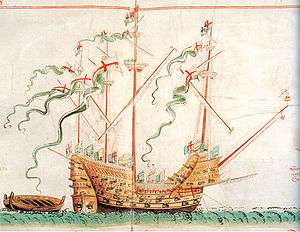 The Henry Grace à Dieu as depicted in the Anthony Roll. | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Henry Grace à Dieu (from 1547 Edward) |
| Builder: | Woolwich Dockyard |
| Launched: | 1514 |
| Commissioned: | 1514 |
| Refit: | rebuilt circa 1536 |
| Honours and awards: | Battle of the Solent |
| Fate: | Unknown, last mentioned in 1553 |
| General characteristics | |
| Tons burthen: | 1000 |
| Length: | 165 ft (50 m) |
| Complement: | 700 - 1,000 |
| Armament: | 43 cannons, 141 swivel guns |
Henry Grace à Dieu ("Henry Grace of God"), also known as Great Harry, was an English carrack or "great ship" of the King's Fleet in the 16th century. Contemporary with the Mary Rose, Henry Grace à Dieu was even larger. The Great Harry was Henry VIII's flagship. She had a large forecastle four decks high, and a stern castle two decks high. She was 165 feet (50 m) long, weighing 1,000–1,500 tons and having a complement of 700–1,000 men. It is said that she was ordered by Henry VIII in response to construction of the Scottish ship Michael, launched in 1511.
History

Built at Woolwich Dockyard from 1512 to 1514, she was one of the first vessels to feature gunports and had twenty of the new heavy bronze cannon, allowing for a broadside. She was fitted out later in the Naval Dockyard in Erith.[1] In all she mounted 43 heavy guns and 141 light guns. She was the first English two-decker and when launched she was, at 1500 tons burthen, the largest and most powerful warship in Europe.
Very early on it became apparent that the ship was top heavy. She was plagued with heavy rolling in rough seas and her poor stability adversely affected gun accuracy and general performance as a fighting platform. To correct this, she underwent a substantial remodeling in Erith in 1536 (the same year as Mary Rose), during which the height of the hull was reduced. In this new form she was 1000 tons burthen and carried 151 guns of varying size, including 21 of bronze; her full crew was reduced to between 700 and 800. She was given an improved and innovative sailing arrangement with four masts, each divided into three sections; the forward two square rigged with mainsail, topsail and topgallants; and the aft two carrying five lateen sails between them. This allowed for easier handling of the sails and spread wind forces more evenly on the ship, resulting in better speed and maneuverability, and allowing better use of the heavy broadside. The only surviving contemporary depiction of the craft is from the Anthony Roll.[2]

Henry Grace à Dieu saw little action. She was present at the Battle of the Solent against French forces in 1545, in which the Mary Rose sank. Overall, she was used more as a diplomatic vessel, taking Henry VIII to the summit with Francis I of France at the Field of the Cloth of Gold.
After the accession of Edward VI in 1547, she was renamed for him. Her fate is uncertain; she may have been destroyed by fire at Woolwich in 1553,[3] or ended up as a discarded hulk on the bank of the River Thames.
The tradition maintained by the Royal Navy of "showing the flag" at seaside towns to uphold the morale of the Navy is said to have its origins in a service held at the Bradstowe Chapel (Broadstairs, Kent) in 1514. The crew of Henry Grace à Dieu attended, whilst their ship, the largest and latest addition to the King's Fleet, was moored nearby.
See also
Henry V's the Grace Dieu 1418
References
- ↑ "A History of South London Suburbs". Ideal Homes. Retrieved 2015-02-01.
- ↑ Lausanne, Edita. The Great Age of Sail, Patrick Stephens Ltd, 1967, p51.
- ↑ Strype, John, Ecclesiastical Memorials, vol. 3 part 1, (1822), 34, dates fire 25 August 1553.
- Lincoln P. Paine (1997) Ships of the World: An Historical Encyclopedia Houghton Mifflin ISBN 0-85177-739-2