Vascular bundle




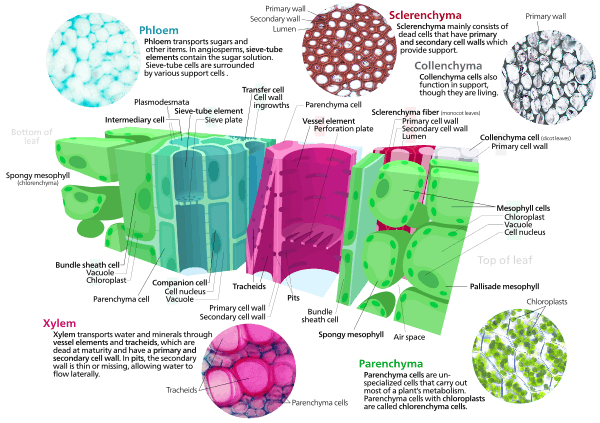
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in vascular tissue, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will include supporting and protective tissues.
The xylem typically lies adaxial with phloem positioned abaxial. In a stem or root this means that the xylem is closer to the centre of the stem or root while the phloem is closer to the exterior. In a leaf, the adaxial surface of the leaf will usually be the upper side, with the abaxial surface the lower side. This is why aphids are typically found on the underside of a leaf rather than on the top, since the sugars manufactured by the plant are transported by the phloem, which is closer to the lower surface.
The position of vascular bundles relative to each other may vary considerably: see stele.
Bundle-sheath cells
Bundle-sheath cells are photosynthetic cells arranged into tightly packed sheaths around the veins of a leaf. They form a protective covering on leaf veins, and consist of one or more cell layers, usually parenchyma. Loosely arranged mesophyll cells lie between the bundle sheath and the leaf surface. The Calvin cycle is confined to the chloroplasts of these bundle sheath cells in C4 plants.
Further reading
- Campbell, N. A. & Reece, J. B. (2005). Photosynthesis. Biology (7th ed.). San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings.
External links
- Curtis, Lersten, and Nowak cross section of a vascular bundle
- Mauseth another cross section of a vascular bundle