2013 Daulat Beg Oldi Incident
| 2013 Daulat Beg Oldi Sector (DBO) Incident | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of China–India relations | |||||||
 Map of Line of Actual Control (LAC) | |||||||
| |||||||
| Commandeers and Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| General Bikram Singh, IA | General Chen Bingde, PLA | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| Northern Command | Lanzhou MR | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| None | None | ||||||
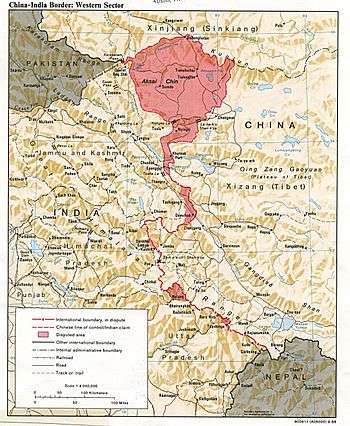
On 15 April 2013, a platoon-sized contingent of the Chinese PLA set up a camp in Raki Nula, 30 km south of Daulat Beg Oldi near the Aksai Chin-Ladakh Line of Actual Control (LAC).[1] Chinese and Indian patrols in this disputed area are common, but both Chinese and Indian military forces have avoided establishing permanent bases and fortifications in the region.[2] Indian forces responded to the Chinese presence by quickly establishing their own encampment 300 meters away. Negotiations between China and India lasted nearly three weeks, during which the Chinese position was reinforced and supported by trucks and helicopters. The dispute was resolved on 5 May, after which both sides withdrew.[3] As part of the resolution, the Indian military agreed to dismantle some military structures 250 km to the south in the disputed Chumar sector that the Chinese perceived as threatening.[4] The Chinese military in July 2014 acknowledged the incursion at the Depsang Valley in Ladakh region and said such incidents occurred due to different perceptions about the Line of Actual Control. [5]
Background
The territorial incident occurred within a 38,000 square kilometre area of disputed territory between India and China, Aksai Chin. The Chinese claim that this area is part of Xinjiang, while the Indians believe that this area is part of Jammu and Kashmir. China and India signed two agreements, in 1993 and 1996, in order to establish protocols to resolve potential disputes in the region. These protocols included the mutual recognition of a "Line of Actual Control" (LAC), but disagreements continue between the two governments about where the LAC lies over a roughly 20 km-wide swath in this sector. India first claimed that the Chinese encampment was 10 km on their side of where they view the LAC, later revising that to 19 km. Despite the disputed area being an "unpopulated and desolate wasteland", it is strategically important to China because of the presence of a highway that connects Pakistan to Tibet and Xinjiang.[6][2] Since the late 1980s, border disputes between India and China have successfully been resolved through diplomacy.[7]
After large-scale Chinese infrastructure improvements adjacent to the region, the Indian army began to develop the infrastructure on their side in the 2000s, which was perceived by the Chinese military as a potential threat.[8] The Indian government claims that Chinese troops continue to illegally enter the area hundreds of times every year. Most of these occur without incident, but in 2011 Chinese military forces entered 18 km into the disputed area in order to dismantle "17 structures made up of loose stones in the shape of bunkers".[9]
Incident
Military deployments
On 15 April 2013, a platoon of 50 Chinese troops established an encampment of four tents 30 km southeast of Daulat Beg Oldi [1] at about 16,300 feet in elevation in the Raki Nala valley. [10] This encampment was discovered the next day by the Indo-Tibetan Border Police, who then set up an encampment of their own consisting of eight tents 300 meters away from the Chinese. The Chinese force was supported by trucks and helicopters.[6] The Indian government considered this the most serious border incident in years.[11]

The Indian military followed a policy of restraint, attempting to keep the issue "localized" and "tactical", in order to give the Indian government the opportunity to resolve the issue through diplomacy. Throughout the incident no shots were fired and the Indian military did not attempt to outflank the Chinese. Minimal efforts were made by the Indian army to reinforce the position after its initial deployment, though the two sides did raise banners encouraging each other to withdraw. Much of the negotiations were conducted between officers present in the two camps.[7] Western media largely interpreted China's actions as a show of force by the Chinese military, but some journalists speculated that the incident was possibly conducted by the Chinese military as a way to protest the perceived existence of a "permanent facility" that the Indian army had built in a disputed area.[2] China's Military think tank later tried to suggest that the incident was "accidental" and "not deliberately staged".[12]
Resolution
The Indian government protested diplomatically, asking the Chinese to withdraw their military and to recognise the status quo that existed before the incident.[13] The Chinese responded by publicly denying that there was any border issue, stating that their forces did not cross what they perceived the LAC to be.[14] India opted not to take military action and pressed on with a long-planned visit to China by its foreign minister, Salman Khurshid.[15] Within the Indian Parliament, the government was heavily criticised by the opposition for its handling of the incident [4] who compared it to India's defeat in the 1962 Sino-Indian War. On 3 May, shortly before the dispute was resolved, the Indian parliament was adjourned after opposition members became disruptive, shouting "get China out, save the country".[11]
The negotiations lasted nearly twenty days, during which the Chinese military increased their presence in the region.[6] To resolve the issue, India agreed to a Chinese demand to demolish several "live-in bunkers" in the Chumar sector, 250 km to the south. Other Chinese demands included the demolition of Indian listening and observation posts built along the border, and an end to the undocumented passage of nomadic shepherds into the Chinese side, but it was not clear to what degree India agreed to these demands.[4] Following the resolution of the dispute, the Chinese military withdrew.[6] The standoff ended on 5 May.[11]
See also
References
Notes
- Bagchi, Indrani. "Depsang Bulge Incursion Accidental, Chinese Military Thinktank Says". Times of India. 15 July 2013. Retrieved 16 July 2013.
- Bharti, Jain. "China Sore with Indian Bid to Build Infrastructure along LAC". The Economic Times. 25 April 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- Bukhari, Fayaz, & Bhattacharjya, Satarupa. "India and China Withdraw Troops from Himalayan Face Off". Global Post. 7 May 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- Defense News. "India Destroyed Bunkers in Chumar to Resolve Ladakh Row". Defense News. 8 May 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- Dutta, Sujan. "Battle of Tents and Banners on Border". Telegraph. 26 April 2013.
- Goswami, Namrata. "China's Incursions Show Strategic Blindness". Asia Times Online. 9 May 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- "Chinese Troops Had Dismantled Bunkers on Indian Side of LoAC in August 2011". India Today. 25 April 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- Lee, Peter. "China's Border Rows Mirror Grim History". Asia Times Online. 3 May 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- Pandit, Rajit. "China's Ladakh Incursion Well-planned". Times of India 26 April 2013. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- Pradhan, Bibhudatta, & MacAskill, Andrew. "Indian Foreign Minister to Visit China to Reduce Border Tensions". Bloomberg. 25 April 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
- PTI. "China’s Ladakh Incursion: Restore Status Quo before Incident, Says India". Firstpost. 23 April 2013. Retrieved 11 March 2013.
- Sawant, Gaurav C. "India is No Pushover: Salmand Khurshid". India Today. 26 April 2013. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- "FM: China-India Border Troops Strictly Observe Agreements". Xinhua. 24 April 2013. Retrieved 11 May 2013.